What is RTT call on Android? Imagine a phone call, but instead of just hearing, you’re reading and typing in real-time. That’s the essence of Real-Time Text (RTT) on Android, a revolutionary feature that’s transforming how we communicate. This isn’t your grandma’s text messaging; RTT offers a seamless blend of voice and text, allowing for instant back-and-forth conversation, all while keeping the conversation flowing.
Dive into a world where communication barriers are broken down, and the possibilities for connection are endless.
From its humble beginnings, RTT has grown into a vital tool, especially for those with hearing or speech impairments. Android has consistently refined RTT, integrating it with accessibility features, ensuring that everyone can participate fully in the digital age. This journey through RTT isn’t just about the technology; it’s about the people it serves, the connections it fosters, and the future it’s building, one text-infused call at a time.
So, buckle up, as we explore how these calls work, how to set them up, and the exciting possibilities they unlock.
Understanding RTT (Real-Time Text) on Android

Let’s dive into the world of Real-Time Text (RTT) on Android. It’s a technology designed to make communication more accessible and immediate. Forget the back-and-forth of traditional text messages; RTT offers a more fluid, real-time conversation experience. Think of it as a blend of texting and phone calls, but with text.
Basic Concept of RTT and its Difference from Traditional Text Messaging
RTT transforms the way we communicate, especially for those who rely on text-based interactions. The fundamental concept revolves around the immediate transmission of text as it’s being typed, unlike standard SMS or messaging apps where the entire message is sent only after the ‘send’ button is pressed. This allows for a more dynamic and interactive conversation.The core difference lies in the real-time aspect.
- Real-Time Transmission: With RTT, each character you type is immediately displayed on the recipient’s screen. There’s no waiting for the entire message to be composed. It’s like having a live text conversation.
- Conversation Flow: The flow of an RTT conversation mirrors a phone call. Both parties can see what the other is typing almost simultaneously, allowing for a more natural back-and-forth.
- Comparison to SMS: Traditional SMS requires composing an entire message before sending. The recipient only sees the completed message.
- Comparison to Messaging Apps: While messaging apps have improved with features like “typing indicators,” they still send messages in discrete chunks. RTT provides a continuous stream of text.
Consider this: you’re trying to schedule a doctor’s appointment. With traditional texting, you might send “Can I schedule an appointment?” and wait for a response. With RTT, the doctor’s office can begin typing their response, “Yes, what day works…” while you’re still typing your question. This immediacy streamlines the interaction.
Concise History of RTT on Android
The evolution of RTT on Android has been a story of continuous improvement, driven by the need for accessible communication. Key milestones and updates have shaped its current functionality and widespread availability.
- Early Adoption (circa 2016): The groundwork for RTT began with early implementations on specific devices and through certain carrier networks. These initial trials showcased the potential but faced limitations in compatibility and adoption.
- Android 7.1.1 Nougat (December 2016): Google integrated native RTT support within the Android operating system, marking a significant step forward. This meant RTT functionality became more standardized and accessible across a wider range of devices.
- Expansion and Refinement (2017-Present): Subsequent Android updates have improved RTT’s capabilities. These updates have included enhancements to user interface, integration with the phone dialer, and improved support for various carrier networks and devices.
- Integration with Accessibility Features: RTT has become closely intertwined with Android’s accessibility features, making it easier for users with hearing or speech impairments to utilize the technology.
This history demonstrates a clear trajectory toward enhanced accessibility and usability, making RTT a valuable tool for communication. The continual refinement reflects a commitment to improving the user experience and broadening its availability.
Accessibility Benefits RTT Offers to Users with Hearing or Speech Impairments
RTT offers significant advantages for individuals with hearing or speech impairments, transforming how they communicate. The technology provides a text-based alternative that preserves the speed and immediacy of a phone call.Here’s how RTT benefits users:
- Real-Time Communication: The real-time nature of RTT allows for an interactive exchange, which closely mimics the experience of a phone call. This is particularly helpful for clarifying information or responding to complex questions.
- Visual Feedback: Unlike phone calls, RTT provides visual feedback. Users can see what the other person is typing, reducing the potential for misunderstandings. This is extremely beneficial for individuals who rely on lip-reading or visual cues.
- Integration with Existing Accessibility Features: RTT is designed to work seamlessly with other Android accessibility features, such as screen readers and voice assistants. This integration ensures a cohesive and user-friendly experience.
- Emergency Services Access: RTT facilitates direct communication with emergency services. Users can text details about their situation in real-time, providing critical information even if they cannot speak.
For instance, consider someone who is Deaf. Using RTT, they can contact their doctor’s office and have a conversation, rather than relying on email or intermediaries, improving privacy and allowing for a more direct exchange of information. This empowerment is at the heart of RTT’s accessibility benefits.
How RTT Calls Work
Let’s dive into the inner workings of Real-Time Text (RTT) calls on your Android device. It’s like having a live chat conversation built directly into your phone calls, but how does it actually function behind the scenes? It’s a fascinating blend of technology that ensures smooth, real-time communication.
Establishing an RTT Call on Android
The initiation of an RTT call on an Android device involves a series of interconnected steps, orchestrating a seamless flow of text data. The process begins with the user selecting the RTT option during a call setup.Once the call is established:* The Android device negotiates the use of RTT with the mobile network. This negotiation typically occurs through the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) messages, which manage call setup and teardown.
- If both parties support RTT, the call is established in RTT mode. The voice codec is often disabled, and the primary communication channel shifts to transmitting text data.
- As the user types, the text is immediately packaged into small data packets. These packets are then sent over the network to the recipient.
- On the receiving end, the Android device reconstructs the incoming data packets into a continuous stream of text, displaying it in real-time. This allows for an interactive conversation similar to instant messaging.
- The system uses the mobile network’s existing infrastructure for the transmission of data packets. The device encodes the text and transmits it using the network’s data channels.
Network Requirements for RTT Calls
Supporting RTT calls requires a network infrastructure capable of handling real-time data transmission. Certain network technologies are crucial for enabling this functionality.The primary network requirement is Voice over LTE (VoLTE).* VoLTE provides the necessary infrastructure for RTT calls. It offers high-quality voice and data services over the LTE network, ensuring low latency and reliable data transmission.
- Without VoLTE, the device might revert to older network technologies, such as 3G or even 2G, which might not support RTT or may provide a degraded experience due to slower data speeds and higher latency.
- The network must support the specific protocols and codecs used for RTT, such as the text transmission protocols. These protocols ensure that the text data is encoded and transmitted efficiently and accurately.
- Network operators need to configure their systems to prioritize RTT traffic to maintain real-time performance. This means the network should prioritize the text data packets to minimize delays and ensure the text appears as quickly as possible on the recipient’s screen.
- The network must have sufficient bandwidth to support RTT calls. Insufficient bandwidth can lead to delays or dropped packets, resulting in a poor user experience.
The Role of the Android System in Managing and Transmitting RTT Data
The Android operating system plays a pivotal role in managing and transmitting RTT data, ensuring the seamless operation of RTT calls. Android integrates several components and processes to support this functionality.The key components include:* The Telephony framework: This framework manages all aspects of phone calls, including RTT. It handles the call setup, teardown, and data transmission.
The RTT service
This service is responsible for encoding and decoding the text data, as well as managing the user interface for RTT calls.
The Network stack
This stack handles the transmission of data packets over the network. It ensures that the text data is sent and received correctly.
- The Android system ensures the data is formatted and transmitted efficiently. This includes handling the user interface elements and providing real-time text input and display.
- The system also handles the synchronization of the text data with the audio stream, if the call also includes audio. This ensures that the text and audio are synchronized, providing a coherent communication experience.
- The Android system integrates security measures to protect the privacy of RTT calls. These measures include encryption and authentication, ensuring that the text data is secure during transmission.
- The Android system also handles the interaction with the hardware components of the device, such as the microphone, speaker, and display. This ensures that the RTT calls function correctly on the device.
- The system provides an API for developers to integrate RTT functionality into their applications. This API allows developers to create custom RTT-enabled apps.
RTT and Accessibility Features
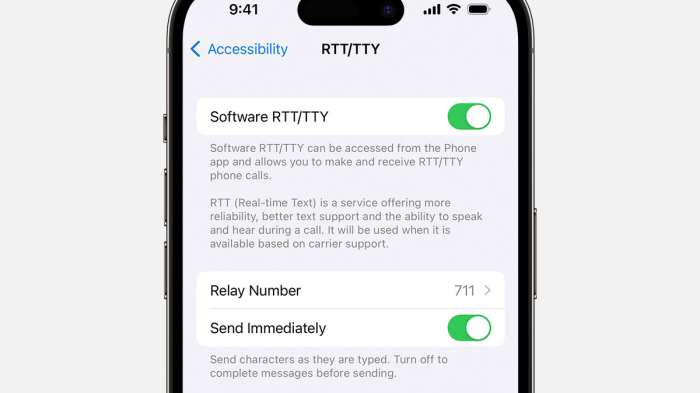
Android’s commitment to accessibility is evident in how Real-Time Text (RTT) seamlessly integrates with its other features, offering a more inclusive communication experience for users with disabilities. This section delves into how RTT works hand-in-hand with accessibility features, user interface considerations, and customization options.
Integration with Other Android Accessibility Features
Android’s design philosophy prioritizes a cohesive user experience, especially when it comes to accessibility. RTT is not an isolated feature; it’s designed to work harmoniously with existing accessibility tools. This ensures that users with various needs can utilize RTT effectively.
- Screen Readers: Screen readers like TalkBack are crucial for visually impaired users. RTT is compatible with screen readers, allowing users to have text messages read aloud as they are typed or received. The screen reader announces each character or word, depending on the user’s settings. The screen reader also provides the user with control over the RTT conversation, enabling the user to start, stop, and manage the conversation.
- Voice Access: For users with mobility impairments, Voice Access provides hands-free control of the device. Users can dictate text for RTT calls, navigate the interface, and manage calls using voice commands. For example, a user could say, “Answer call with RTT” or “Send text to [contact] using RTT”.
- Switch Access: Switch Access allows users to interact with their devices using external switches, such as buttons or joysticks. Users can map actions, including RTT-related functions, to these switches, providing an alternative method of interaction.
- Captioning: While RTT focuses on text-based communication, the system can be integrated with captioning features. This can be beneficial for users who are deaf or hard of hearing, providing a visual representation of spoken content in addition to the RTT text.
User Interface Considerations for RTT
The user interface (UI) is paramount for usability, especially when designing for accessibility. RTT’s UI is designed with ease of use in mind, ensuring that the process of making and receiving RTT calls is intuitive and efficient.
- Clear Visual Cues: The UI provides clear visual indicators to show when an RTT call is active, including distinct icons and notifications. This is particularly important for users with visual impairments who rely on screen readers.
- Text Input and Display: The text input field is designed to be easily accessible, with a large, clear font and sufficient spacing between characters. The text display area is equally clear, showing the conversation in real-time.
- Call Controls: Simple, easily accessible call controls (e.g., answer, end call, mute) are essential. These controls are often placed in prominent locations on the screen and are compatible with screen reader navigation.
- Integration with Dialer: RTT functionality is often integrated directly into the phone dialer app. This allows users to easily initiate RTT calls directly from their contact list or by entering a phone number.
Customizing RTT Settings for Optimal Accessibility
Android provides a range of customization options to tailor the RTT experience to individual needs. These settings empower users to optimize RTT for their specific requirements.
- Enabling/Disabling RTT: Users can easily enable or disable RTT within the phone settings. This allows users to switch between regular voice calls and RTT calls based on their needs.
- Call Preference: Users can set their preferred call type (e.g., always use RTT, ask before each call, never use RTT). This ensures that calls are initiated in the desired mode.
- Font Size and Display: The ability to adjust font size and display settings (e.g., contrast, color schemes) within the RTT interface is crucial for users with visual impairments.
- Notification Settings: Customizable notification settings, including sound and vibration patterns, are available to ensure that users receive timely alerts about incoming RTT calls and messages.
- Screen Reader Integration Settings: Users can customize how screen readers interact with RTT, such as the frequency with which text is announced (character by character, word by word, or sentence by sentence).
Compatibility and Device Support for RTT
Navigating the world of Real-Time Text (RTT) on Android requires understanding the compatibility landscape. It’s not a feature universally available across all devices or Android versions, so knowing where it thrives is key to unlocking its benefits. This section breaks down the Android versions that support RTT, looks at the major players in phone manufacturing and their implementations, and provides a glimpse into the differences you might encounter across various device models.
Android Versions Supporting RTT
RTT support on Android has evolved over time. Early adopters had to wait, but the technology has matured.Android versions with RTT support include:* Android 4.4 (KitKat) and later. However, initial support was limited, and full functionality and widespread adoption became more prevalent in later versions.
- Android 9.0 (Pie) and subsequent versions saw more comprehensive RTT integration. The core Android framework provided better support, making it easier for manufacturers to implement RTT in their devices.
- Android 10, 11, 12, 13, and the latest Android versions continue to refine and enhance RTT capabilities, including improved user interfaces and accessibility features. These updates have expanded compatibility and improved the user experience.
Phone Manufacturers and RTT Implementation
Various phone manufacturers have embraced RTT, integrating it into their devices. The level of implementation can vary, but these are some of the key players:* Google: Google’s Pixel phones have generally offered excellent RTT support, often with seamless integration within the native dialer app and other communication features. They often lead in adopting new Android features, including accessibility tools like RTT.
Samsung
Samsung, a major player in the Android ecosystem, has implemented RTT across many of its Galaxy phones. The integration is typically well-executed, with RTT accessible through the phone app.
Motorola
Motorola has incorporated RTT into its devices, offering users another option for real-time text communication. Motorola’s implementation varies across its range, so it is important to verify support for specific models.
LG (Historically)
While LG is no longer producing phones, their devices also included RTT support in the past. If you have an older LG phone, it is worth checking the settings to see if RTT is available.
Other Manufacturers
Brands like OnePlus, Xiaomi, and others have also begun to support RTT, though the availability and implementation may vary depending on the model and region. Always check the device specifications and settings to confirm RTT functionality.
Comparing RTT Capabilities Across Android Device Models
RTT functionality can differ across Android device models. The following table provides a comparison of RTT capabilities, but remember that specific features and implementations can vary.
| Feature | Google Pixel 7 | Samsung Galaxy S23 | Motorola Edge+ (2023) | Xiaomi 13 Pro |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Android Version | Android 13 (Upgradable) | Android 13 (Upgradable) | Android 13 (Upgradable) | Android 13 (Upgradable) |
| Native Dialer Integration | Excellent, integrated within the phone app. | Good, integrated within the phone app. | Standard, integrated within the phone app. | Varies, check phone app settings. |
| Accessibility Options | Comprehensive, with options for font size, and contrast. | Good, offering adjustments for text display. | Basic, supporting font size adjustment. | Varies, check accessibility settings. |
| User Interface | Clean and intuitive, with easy access to RTT features. | User-friendly, with RTT easily accessible during calls. | Functional, with RTT controls available during calls. | Varies, user experience dependent on phone app design. |
| Call Quality | High, leveraging Google’s network optimization. | High, dependent on carrier network. | Good, dependent on carrier network. | Varies, dependent on carrier network. |
The table demonstrates that the implementation and integration of RTT can vary. While all listed devices support RTT, the user experience, accessibility features, and overall integration can differ.
RTT and Emergency Services
In the realm of mobile communication, particularly on Android, the integration of Real-Time Text (RTT) with emergency services represents a critical advancement in accessibility and safety. This section delves into how RTT facilitates communication during emergencies, explores the inherent challenges, and provides practical guidelines for effective utilization.
Using RTT to Contact Emergency Services
When a crisis unfolds, the ability to swiftly and clearly communicate is paramount. RTT empowers individuals, especially those with hearing or speech impairments, to connect with emergency responders.To initiate an RTT call to emergency services on Android:* Dial the emergency number (e.g., 911 in the US).
- The phone, if RTT-enabled and configured, will automatically attempt to establish an RTT connection.
- The user can then type their message in real-time, and the emergency dispatcher receives the text as it is being typed.
- This allows for a continuous, two-way flow of information, enabling the user to provide critical details such as location, the nature of the emergency, and any other relevant information without relying solely on voice.
The implementation of RTT for emergency calls aims to bridge the communication gap, ensuring that everyone can access help when needed.
Challenges and Considerations for RTT in Emergency Situations, What is rtt call on android
While RTT offers significant advantages, several challenges and considerations exist when it comes to its use in emergency scenarios. These factors necessitate careful attention and proactive solutions.* Network Compatibility: The effectiveness of RTT hinges on network support. In areas with poor or limited network coverage, RTT calls may be unreliable or fail altogether. This underscores the need for robust network infrastructure and ongoing improvements.
Dispatcher Training
Emergency dispatchers require specialized training to effectively handle RTT calls. They must be proficient in reading and responding to real-time text, managing the flow of information, and ensuring accurate interpretation.
Location Accuracy
Determining the precise location of the caller is crucial in emergencies. While RTT allows for text-based communication of location information, it may not be as immediate or precise as location data transmitted via voice calls. Therefore, the integration of location services with RTT is vital.
Interoperability
Ensuring seamless interoperability between different mobile devices, networks, and emergency service systems is critical. Standardized protocols and communication formats are essential to avoid compatibility issues.
Device Configuration
Users need to have RTT properly configured on their devices. This includes enabling RTT in the phone settings and ensuring the device supports RTT calls.
User Proficiency
Users should be familiar with using RTT and be able to type quickly and accurately, particularly in high-pressure situations.Addressing these challenges is vital to maximizing the effectiveness of RTT in emergency situations and ensuring the safety of all users.
Best Practices for Using RTT to Communicate with Emergency Responders
To maximize the effectiveness of RTT during emergencies, adopting best practices is essential. These guidelines will help users communicate effectively and efficiently with emergency responders.* Pre-Emergency Preparation:
Familiarize yourself with your phone’s RTT settings and how to initiate an RTT call.
Practice typing short, clear messages.
Store your address and other important information in a readily accessible format.
During the Emergency
Clearly state your location at the beginning of the call.
Provide concise and accurate information about the emergency.
Describe the situation, the number of people involved, and any immediate needs.
Stay calm and avoid unnecessary information.
Wait for the dispatcher to respond before providing additional information. –
Post-Emergency
Follow the instructions provided by the emergency responders.
Provide any additional information requested.
Save the call logs for future reference if necessary.
By adhering to these best practices, individuals can significantly improve their ability to communicate effectively with emergency services using RTT, thereby increasing the likelihood of a positive outcome.
Troubleshooting Common RTT Issues: What Is Rtt Call On Android
Dealing with Real-Time Text (RTT) on your Android device can sometimes feel like navigating a maze. From unexpected glitches to frustrating communication breakdowns, encountering issues is, unfortunately, a part of the experience. This section dives into the common problems you might face and offers practical solutions to get you back on track, ensuring smooth and reliable RTT communication.
RTT Not Working
If RTT isn’t functioning as expected, several factors could be at play. The good news is that most issues are easily resolved with a bit of troubleshooting.
- Compatibility Concerns: Verify that both your device and the person you’re communicating with support RTT. Older devices or those running outdated software may not have the necessary features. Check your device’s settings to ensure RTT is enabled. Your contacts also need to have compatible devices.
- Network Connectivity Problems: RTT relies on a stable network connection. Poor signal strength or intermittent connectivity can disrupt the real-time text exchange. Try moving to a location with better reception or switching to Wi-Fi if available.
- App-Specific Glitches: Occasionally, the phone app itself might experience a temporary glitch. Try closing and reopening the app or, if necessary, restarting your device.
- Software Updates: Ensure your Android operating system and the phone app are up to date. Updates often include bug fixes and performance improvements that can resolve RTT issues. Check for updates in your device settings.
- Incorrect Settings: Double-check your RTT settings. Make sure RTT is enabled and configured correctly. Some settings may need to be adjusted based on your carrier or personal preferences.
Poor Call Quality
Just like with regular voice calls, RTT calls can suffer from poor quality, impacting the readability and speed of communication. This can be particularly frustrating when trying to convey important information.
- Network Congestion: During peak hours, network congestion can lead to delays and dropped text segments. Try making the call during off-peak hours or in an area with less network traffic.
- Signal Interference: Physical obstructions, such as buildings or walls, can interfere with the signal, leading to poor call quality. Try moving to a location with a clearer line of sight to the cell tower.
- Device Issues: Problems with your device’s microphone or speaker can affect the quality of the RTT experience. Ensure that your device’s audio components are functioning correctly. Consider using a headset or speakerphone to improve clarity.
- Carrier-Specific Problems: Occasionally, the issue might stem from problems with your carrier’s network. Contact your carrier to report the issue and inquire about any known outages or performance issues in your area.
- Codec Compatibility: The codecs used for audio and text transmission can affect call quality. Ensure that your device and the other party’s device support compatible codecs. Incompatible codecs may lead to degraded audio and text quality.
Missing Text
Lost or incomplete text messages can make RTT communication challenging. Identifying and addressing the causes of missing text is crucial for effective communication.
- Network Instability: Intermittent network connectivity is a common culprit. Even brief interruptions can cause text segments to be dropped. Monitor your network signal strength and move to a location with a more reliable connection.
- Device Processing Delays: If your device is running multiple applications simultaneously, it may struggle to process RTT messages in real-time. Close unnecessary apps to free up system resources.
- Character Limits: Some RTT implementations might have character limits per message segment. If you’re typing long sentences, they might be truncated. Keep your messages concise.
- Software Bugs: Software glitches can occasionally lead to text being lost or delayed. Ensure your device’s operating system and the phone app are up to date. Restarting your device can often resolve temporary software issues.
- Recipient’s Device Problems: The issue might not be on your end. The recipient’s device could be experiencing connectivity problems or software glitches that are causing them to miss text. Ask the recipient to troubleshoot their device.
RTT Troubleshooting Flowchart
To help you diagnose and resolve RTT-related problems systematically, here’s a flowchart you can follow. This visual guide will lead you through a series of questions and actions to identify and fix common issues.
Imagine a flowchart that starts with a box labeled “RTT Not Working?” This is the starting point.
Step 1:If the answer is “Yes,” the flowchart branches out.
The first branch asks, “Is RTT enabled in settings?” If the answer is “No,” the flowchart directs you to “Enable RTT in settings.” If the answer is “Yes,” the flowchart continues to the next question.
Step 2:The next question is, “Is the other party’s device RTT compatible?” If the answer is “No,” the flowchart advises, “Ensure the other party’s device supports RTT.” If the answer is “Yes,” the flowchart moves on.
Step 3:Next, the flowchart asks, “Is the network connection stable?” If the answer is “No,” it advises, “Move to an area with better signal/switch to Wi-Fi.” If the answer is “Yes,” the flowchart continues.
Step 4:The next question is, “Is the phone app up to date?” If the answer is “No,” the flowchart guides you to “Update the phone app.” If the answer is “Yes,” the flowchart moves forward.
Step 5:Finally, the flowchart asks, “Restart your device?” If the answer is “Yes,” it instructs, “Restart your device.” If the issue persists, the flowchart directs you to contact your carrier for support.
Alternative Flow:If at the start, “RTT Not Working?” the answer is “No,” then the flowchart directs you to “Check for Poor Call Quality or Missing Text”.
For Poor Call Quality:This section asks:
“Is the network congested?” If “Yes,” try calling during off-peak hours.
“Is there signal interference?” If “Yes,” move to a better location.
“Are device’s audio components working?” If “No,” check your device.
“Contact Carrier” for other issues.
For Missing Text:This section asks:
“Is the network unstable?” If “Yes,” move to a better location.
“Is your device overloaded?” If “Yes,” close unnecessary apps.
“Are messages too long?” If “Yes,” shorten messages.
“Are software bugs present?” If “Yes,” update/restart device.
“Is the recipient experiencing issues?” If “Yes,” ask them to troubleshoot.
RTT vs. Other Communication Methods
Let’s dive into how RTT stacks up against the usual suspects in the communication world: SMS, MMS, and video calls. It’s a bit like comparing apples, oranges, and maybe a high-definition grapefruit – each has its own unique flavor and appeal. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each helps you choose the right tool for the job.
Comparing Communication Methods
We’ll explore how RTT measures up against the other communication methods, including SMS, MMS, and video calls, in a comparative table. This table will highlight the key advantages and disadvantages of each method, providing a clear overview to help you determine the most appropriate option for different scenarios.
| Communication Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|---|
| RTT (Real-Time Text) |
|
|
|
| SMS (Short Message Service) |
|
|
|
| MMS (Multimedia Messaging Service) |
|
|
|
| Video Calls |
|
|
|
Scenarios Where RTT Shines
RTT excels in specific situations where other communication methods fall short. Consider the following scenarios where RTT is the clear winner.
- Emergency Services: Imagine a scenario where a person is in a life-threatening situation and unable to speak due to a medical condition or environmental factors. RTT enables them to quickly and discreetly communicate their location and situation to emergency services, potentially saving their life. This is particularly crucial for individuals who are deaf or hard of hearing.
- Noisy Environments: Picture yourself at a loud concert or a construction site. A voice call would be practically impossible. With RTT, you can exchange information without yelling over the din. This silent communication is a game-changer in noisy environments.
- Discreet Communication: Imagine you are in a meeting, and you need to communicate with someone without disrupting the proceedings. RTT offers a way to silently exchange information, making it perfect for sensitive discussions.
- Accessibility: For individuals with hearing or speech impairments, RTT provides a vital bridge to communication. It ensures that they can participate fully in conversations and access essential services, fostering inclusivity.
The Future of RTT on Android
The world of communication is perpetually evolving, and RTT on Android is poised to be a significant player in that evolution. As technology advances, we can anticipate exciting developments that will refine and expand RTT’s capabilities, making it even more accessible and user-friendly for everyone. This includes potential integration with new technologies and platforms, creating a more inclusive and connected digital landscape.
Potential Future Developments and Enhancements for RTT on Android
The ongoing evolution of RTT promises exciting advancements. We can anticipate several key areas of improvement and expansion.
- Enhanced User Interface and Experience: Expect a more intuitive and visually appealing RTT interface. This could involve improved text formatting options, better integration with contact lists, and customizable display settings to cater to individual preferences and accessibility needs. The goal is to make RTT as seamless and natural as a standard phone call. Imagine a streamlined interface that allows for quick access to frequently used phrases and emoticons, enhancing the richness of communication.
- Advanced Predictive Text and Autocorrect: Future RTT systems will likely incorporate more sophisticated predictive text and autocorrect functionalities. This could include context-aware suggestions, personalized dictionaries that learn user vocabulary, and improved accuracy in understanding slang, dialects, and technical jargon. This would significantly speed up text entry and reduce the potential for misunderstandings.
- Multimedia Integration: RTT might evolve to support multimedia elements. Think about the possibility of easily sharing images, short video clips, or even audio snippets within an RTT conversation. This would transform RTT from a text-only medium to a richer, more expressive form of communication, mirroring the capabilities of modern messaging apps. This could include the ability to annotate images or add captions to enhance clarity and context.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Future developments may focus on making RTT more interoperable with other platforms and devices. This could involve seamless integration with desktop computers, tablets, and smartwatches, allowing users to initiate and continue RTT conversations across multiple devices without interruption. This would provide greater flexibility and convenience for users, regardless of the device they are using.
- Improved Accessibility Features: RTT will continue to enhance accessibility features. This could include improved screen reader compatibility, adjustable text sizes and color schemes, and integration with assistive technologies. The aim is to ensure that RTT remains fully accessible to people with disabilities. Consider the possibility of real-time translation capabilities, breaking down language barriers and facilitating communication across diverse communities.
How RTT Might Evolve with Emerging Technologies, Like 5G
The advent of 5G technology is set to revolutionize communication, and RTT stands to gain significantly from these advancements. The enhanced speed, bandwidth, and reduced latency of 5G will unlock new possibilities for RTT.
- Faster and More Reliable Connections: 5G’s superior network capabilities will translate into faster and more reliable RTT connections. This means that text will appear in real-time with minimal delay, making conversations feel more natural and fluid. This is particularly crucial for emergency situations where every second counts.
- Enhanced Audio and Video Integration: The increased bandwidth of 5G will open doors for better integration of audio and video features within RTT. Imagine the possibility of incorporating short video messages or live audio snippets during an RTT call, enriching the communication experience. This could provide a more dynamic and engaging way to communicate.
- Improved Location Services: 5G’s improved location accuracy could be leveraged to provide more context-aware RTT services. For example, in an emergency, the user’s location could be automatically shared with emergency services, improving response times. The accuracy of location data would be a significant advantage in providing assistance.
- Wider Coverage and Accessibility: 5G networks are being deployed worldwide, expanding the reach of RTT to more areas and devices. This broader coverage will ensure that more people can benefit from RTT, regardless of their location. This will enhance accessibility, especially in remote or underserved areas.
- Integration with IoT Devices: 5G could enable RTT to integrate with the Internet of Things (IoT). Imagine being able to control smart home devices or receive real-time updates from wearable technology during an RTT call. This integration could provide a new layer of functionality and convenience for users.
Share Insights on How RTT Could Be Integrated with Other Communication Platforms
The potential for RTT to integrate with other communication platforms is vast, paving the way for a more unified and accessible communication ecosystem.
- Integration with Messaging Apps: RTT could be integrated with popular messaging apps like WhatsApp, Telegram, and Signal. This would allow users to seamlessly switch between text messaging and RTT within the same app, providing a consistent and user-friendly experience. This integration would significantly increase the accessibility of RTT for a wider audience.
- Integration with Video Conferencing Platforms: RTT could be incorporated into video conferencing platforms like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Google Meet. This would allow users to use RTT for real-time text-based communication during video calls, providing an alternative communication channel for individuals who are deaf, hard of hearing, or in noisy environments. This would greatly improve inclusivity in virtual meetings.
- Integration with Social Media Platforms: RTT could be integrated into social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter. This could enable users to communicate with each other in real-time using text, providing an alternative to voice or video calls. This could be particularly useful for people who prefer text-based communication or who have accessibility needs.
- Unified Communication Systems: RTT can be integrated into unified communication systems used by businesses. This would allow employees to communicate using RTT, alongside other forms of communication, such as voice calls and video conferencing. This would improve collaboration and communication within organizations, ensuring that all employees can participate fully.
- Emergency Communication Systems: RTT could be integrated into emergency communication systems, such as 911 services. This would enable individuals who are unable to use voice calls to contact emergency services via text. This integration would be crucial for ensuring that everyone can access emergency services, regardless of their communication preferences or abilities.
