Uninstall android studio from mac – Uninstalling Android Studio from your Mac might seem like a simple task, but beneath the surface lies a treasure trove of files, settings, and dependencies waiting to be unearthed. We’re embarking on a digital archaeological dig, a quest to completely eradicate Android Studio from your system, leaving no trace behind. This isn’t just about dragging an icon to the trash; it’s about understanding the intricate ecosystem that Android Studio builds on your Mac and how to dismantle it brick by digital brick.
We’ll start by pinpointing exactly where Android Studio has set up shop, navigating through its secret hideouts within your Applications folder and beyond. Then, we’ll arm ourselves with the tools needed to perform the ultimate act of digital decluttering. From the straightforward drag-and-drop method to the more sophisticated command-line approach, we’ll ensure you’re equipped for any uninstallation challenge. Consider this your personal guide to liberating your Mac from the clutches of the Android development environment.
Identifying Android Studio Installation Location on macOS
Alright, let’s get down to brass tacks. You’re about to evict Android Studio from your Mac, and to do that effectively, you need to know where it’s hiding. This isn’t some high-stakes detective novel, but rather a straightforward process of locating the key components. Understanding the installation directories is crucial for a clean and complete uninstallation.
Locating the Android Studio Application File
Finding the Android Studio application file is usually pretty simple. It’s like looking for your keys; you probably left them in the most obvious place.The most common location is within your Applications folder. You can use the following command in the Terminal to locate it directly:
/Applications/Android Studio.app
This command gives you the direct path to the application bundle. You can also visually confirm its presence by navigating to your Applications folder in Finder. The Android Studio application file will be there, usually with the iconic green and blue Android logo.
Typical Directory Structures for Android Studio Components
Android Studio doesn’t just plop down a single file; it’s a collection of parts, scattered across your system. Knowing where these components reside is essential for a thorough removal. The directory structure is designed for organization, but for our purposes, we’re after everything.The main areas you’ll want to investigate include:
- Applications Folder: This is where the primary application bundle resides, as we discussed. It contains the core executable and related resources.
- User Home Directory (~/): Several important configuration files and settings are stored within your user home directory. This includes:
~/Library/Application Support/Google/AndroidStudio...: Contains various Android Studio settings, caches, and potentially project-specific data.~/Library/Preferences/com.google.android.studio...: Holds the preferences and settings for Android Studio.~/Library/Caches/AndroidStudio...: Cache files used by Android Studio.- Android SDK Location: The Android SDK (Software Development Kit) is a critical component for developing Android apps. The SDK includes tools, libraries, and the Android platform. We’ll delve into the SDK’s location in more detail below.
- Gradle Caches: Gradle is the build system used by Android Studio. Its caches are usually stored in a directory within your user home directory, often under a folder like
.gradle. These caches store downloaded dependencies and build artifacts.
Finding the Android SDK and Associated Files
The Android SDK is the heart of Android development, housing the tools, platform, and libraries that allow you to build and test applications. Its location is crucial for removing everything associated with Android Studio. The default location, when you first install Android Studio, is typically in the following directory:
- Default SDK Location: Usually, the SDK resides in
~/Library/Android/sdk. However, this can vary based on your installation choices.
You can determine the exact location of your SDK within Android Studio itself:
- Open Android Studio.
- Go to “Android Studio” (in the menu bar) -> “Settings” (or “Preferences” on macOS).
- In the Settings/Preferences window, navigate to “Appearance & Behavior” -> “System Settings” -> “Android SDK”.
- The “Android SDK Location” field will display the directory where your SDK is installed.
This method ensures you identify the correct SDK directory, even if you’ve customized your installation. It’s like having a map to your own treasure.Additionally, consider the following files and directories associated with the SDK:
- SDK Platform Tools: These tools are essential for building, testing, and debugging Android apps. They are usually found within the SDK directory, in a subfolder named “platform-tools.”
- SDK Build Tools: These tools are responsible for the build process, compiling resources, and packaging your application. They reside within the SDK directory, in a subfolder called “build-tools,” with versions for different Android API levels.
- SDK Platforms: This directory contains the Android platform versions you’ve installed, each containing the Android system images and libraries for different API levels. They are located within the SDK directory, in a subfolder named “platforms.”
- Emulator Images: If you’ve used the Android emulator, the virtual device images are stored within the SDK directory, typically in a subfolder named “system-images” or within the AVD (Android Virtual Device) directory, usually located at
~/.android/avd/.
Knowing the location of these components ensures you remove all associated files during the uninstallation process. It’s like dismantling a well-oiled machine; you need to take each part apart systematically.
Methods for Uninstalling Android Studio
Removing Android Studio from your Mac is a necessary task at times, whether you’re upgrading, troubleshooting, or simply decluttering your system. Luckily, there are a few straightforward methods to accomplish this, each catering to different preferences and levels of technical comfort. Let’s delve into the ways you can bid farewell to the Android development environment, ensuring a clean and efficient uninstallation.
Drag-and-Drop Method, Uninstall android studio from mac
This is the simplest and most user-friendly approach, perfect for those who prefer a visual and intuitive method. It involves manually moving the Android Studio application to the Trash.To begin the process, navigate to your Applications folder. Locate the Android Studio application icon. This icon typically resembles a stylized blue and white Android robot head. Now, click and drag the Android Studio icon directly to the Trash icon, which is usually located in the Dock at the bottom of your screen.
This action essentially marks the application for deletion. Once the icon is in the Trash, release the mouse button. The application is now ready for removal, but it’s not completely gone yet.Next, right-click (or Control-click) on the Trash icon in the Dock. A contextual menu will appear. From this menu, select “Empty Trash.” macOS will then prompt you to confirm the deletion.
Be absolutely certain that you wish to remove the application, as this action is irreversible. After confirming, macOS will begin the process of removing the Android Studio application and all of its associated files from your system. This method is the quickest way to initiate the uninstallation. However, it’s important to know that this approach may not remove all associated files and configurations.
You might still have residual files scattered throughout your system. Therefore, for a truly thorough removal, you may need to use the command-line method or a dedicated uninstaller tool.
Using the Command Line (Terminal) for Complete Removal
For a more comprehensive uninstallation, particularly when dealing with stubborn files or wanting to ensure every trace is gone, the command line offers a powerful solution. This method requires a little more technical know-how, but it provides greater control over the uninstallation process.Before proceeding, open the Terminal application. You can find it in the Utilities folder within your Applications folder.
Once Terminal is open, you will be presented with a command prompt.The first step is to locate and remove the Android Studio application itself. You’ll use the `rm` command, which stands for “remove,” along with the path to the application. The path will usually be `/Applications/Android Studio.app`. So, the command to use is:
sudo rm -rf /Applications/Android\ Studio.app
Type this command into the Terminal and press Enter. You will be prompted to enter your administrator password. This is necessary because the `sudo` command grants elevated privileges, allowing you to delete files that require administrator access.After entering your password (and noting that the password entry will not display any characters on the screen for security reasons), press Enter again.
The application should now be removed. The `-rf` flags are important here: `-r` stands for “recursive,” meaning the command will delete the application and all its contents, and `-f` stands for “force,” which means it will proceed even if it encounters any errors.Next, you need to remove any associated configuration files, caches, and preferences that might be scattered throughout your system.
These files are typically located in your user’s home directory. Here are some key directories to check:
~/Library/Application Support/AndroidStudio*: This directory often contains plugin configurations and other supporting files.~/Library/Caches/AndroidStudio*: This directory contains cached data.~/Library/Preferences/com.google.android.studio.*.plist: This contains preference files.~/Library/Preferences/AndroidStudio*: Other preference files.
To remove these directories and files, use the `rm` command again, along with the appropriate paths. For example, to remove the application support directory, you would use the following command:
sudo rm -rf ~/Library/Application\ Support/AndroidStudio*
Remember to replace `AndroidStudio*` with the actual name of the directory or file if necessary. Be cautious when using the `rm` command, as deleting the wrong files can potentially cause problems with your system.After removing these files, you may also want to delete the Android SDK and any virtual devices you’ve created. The SDK is usually located in a directory named `Android` in your home directory or the `Library` folder.
Use the `rm` command to remove these directories, just as you did for the application and configuration files.Finally, after completing these steps, you might consider restarting your Mac to ensure that all changes are fully applied. While this isn’t strictly necessary, it can help clear any lingering processes or caches. Using the command line offers a more thorough uninstallation than the drag-and-drop method.
Uninstalling Android Studio Using a Dedicated Uninstaller Tool
While not always available, some developers provide dedicated uninstaller tools to streamline the removal process. These tools automate the steps involved in uninstalling Android Studio, making it easier and safer for users. If a dedicated uninstaller is available, it’s often the most convenient method.If a dedicated uninstaller is provided by the Android Studio developers, it’s typically available as a separate download or bundled with the application itself.
The availability of such a tool is highly dependent on the version of Android Studio and the preferences of its developers.To use the uninstaller, download and run it. The tool will usually guide you through the removal process. This may involve selecting the components you wish to uninstall, such as the Android Studio application, SDK, and configuration files. The uninstaller will then automatically remove these components from your system.
This approach simplifies the process and reduces the risk of accidentally deleting the wrong files.Dedicated uninstallers often provide a more complete removal than the drag-and-drop method, as they are specifically designed to target all associated files and configurations. Furthermore, they are generally safer to use than the command-line method, as they minimize the risk of user error. The user interface typically presents a list of components to remove, with clear instructions.
Removing Android Studio Components and Associated Files
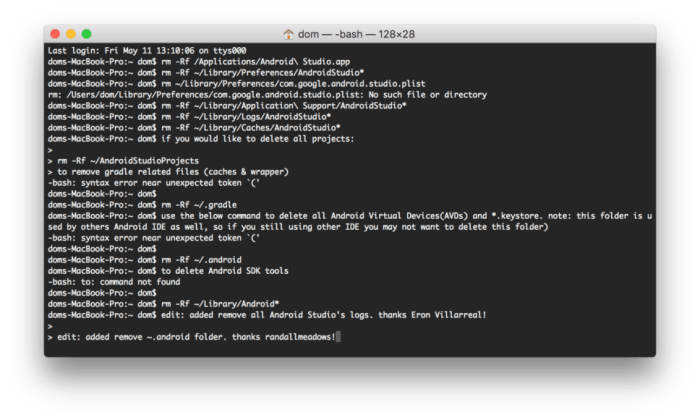
Now that you’ve successfully uninstalled Android Studio, it’s time to perform a thorough cleanup. This involves removing the remnants of the application to free up valuable disk space and ensure a clean slate for future installations or a complete removal. Think of it as spring cleaning for your Mac, but instead of dusting furniture, you’re deleting digital clutter. This meticulous process helps to prevent conflicts and ensures your system remains optimized.
Directories and Files to Remove After Uninstalling Android Studio
After uninstalling Android Studio, a multitude of files and directories are often left behind. These files range from project caches to settings files, and removing them ensures a complete removal of the application. Here’s a breakdown of the common locations where these files might reside:
- Android Studio Application Directory: While you’ve uninstalled the application itself, remnants might persist. Double-check that the Android Studio application directory in /Applications/ is completely empty.
- Android SDK Directory: If you installed the Android SDK separately, it typically resides in your home directory or a dedicated location. By default, it’s often located at `~/Library/Android/sdk`. This directory contains the Android SDK Platform tools, build tools, and other components.
- Gradle Caches: Gradle, the build system used by Android Studio, stores caches in a specific directory. These caches can consume a significant amount of space. You can find these caches at `~/.gradle/caches`.
- Project-Specific Files: If you’ve created any Android projects, their associated files and directories will remain. These will be in the locations you saved your projects.
- User-Specific Configuration Files: Configuration files containing your preferences, settings, and other user-specific data are often stored in your home directory. These are typically located in the `.AndroidStudio
` directory.
Deleting Android Studio Preferences and Cache Files
Cleaning up preferences and cache files is crucial for a complete removal and can help resolve potential issues during future installations. These files store your personalized settings and cached data, which, if left behind, might interfere with new installations or settings.Here’s a step-by-step procedure to delete Android Studio preferences and cache files:
- Locate the Preference Directory: Open Finder and navigate to your home directory (represented by the house icon in the sidebar). Press `Command + Shift + .` (period) to reveal hidden files and folders. This will allow you to see the hidden directories like `.AndroidStudio
`. - Identify the Android Studio Version: The directory containing your preferences is named `.AndroidStudio
`, where ` ` is the specific version of Android Studio you were using (e.g., `.AndroidStudio2022.1`). - Delete the Preference Directory: Drag the entire `.AndroidStudio
` directory to the Trash. This action removes all of your custom settings, plugins, and configurations. - Locate the Cache Directory: The cache directory, which stores temporary files and data, is usually located at `~/Library/Caches/Google/AndroidStudio
`. - Delete the Cache Directory: Drag the entire `AndroidStudio
` directory within the `~/Library/Caches/Google/` directory to the Trash. This clears cached data and helps to reclaim disk space. - Empty the Trash: Once you’ve moved the preference and cache directories to the Trash, empty the Trash to permanently delete these files and free up disk space.
Important Note: Deleting these files will remove your customized settings. However, it also guarantees a clean start for future installations and can resolve issues that may arise from outdated settings.
Common Android Studio-Related Files in the User’s Home Directory
Your home directory acts as the central hub for user-specific data, and Android Studio frequently stores various files there. Understanding where these files reside allows for a comprehensive cleanup after uninstallation.Here’s a list of common Android Studio-related files and directories you might find in your home directory:
- `.AndroidStudio
`: As previously mentioned, this hidden directory contains your preferences, settings, and plugins. - `.gradle`: This directory holds Gradle-related configuration files and caches, critical for project builds.
- `.android`: This directory stores Android-related settings, such as the `avd` (Android Virtual Device) directory, which contains virtual device configurations.
- `AndroidStudioProjects`: This directory (or the custom location you specified) houses your Android project files.
- SDK-related files: This includes `platforms`, `platform-tools`, `tools`, `build-tools`, and other SDK components, often found in the `~/Library/Android/sdk` directory.
- Emulator related files: If you used the Android Emulator, it might leave behind configuration files and snapshots in your home directory. The exact location can vary depending on your setup.
Cleaning Up the Android SDK and Emulator Data

After successfully bidding farewell to Android Studio, it’s time to perform a final, crucial cleaning operation. This involves removing the remnants of the Android SDK and emulator data, ensuring a truly clean slate. This is akin to tidying up your workshop after a project; you wouldn’t want stray tools and materials cluttering up the space. The following steps will guide you through this process, leaving your system free of lingering Android development footprints.
Removing the Android SDK
The Android SDK is the heart of Android development, containing the tools, platforms, and libraries necessary to build apps. Removing it ensures that no outdated components remain on your system. Before starting, it is good practice to back up any critical data or project files.To remove the Android SDK, follow these steps:
- Locate the SDK directory. The default location is usually within your user directory, often found at
~/Library/Android/sdk. However, the installation location may vary depending on your setup. If you’re unsure, check the settings within Android Studio before uninstalling, or search your entire hard drive. - Delete the SDK directory. Once you’ve located the SDK directory, you can delete it. This will remove all SDK components, including platforms, build tools, and other dependencies. You can do this by dragging the folder to the trash or using the command line with the
rm -rfcommand (be very careful with this command, as it permanently deletes files). For example:
rm -rf ~/Library/Android/sdk - Remove any environment variables. After deleting the SDK directory, remove any environment variables related to the Android SDK from your
.bashrc,.zshrc, or other shell configuration files. These variables, such asANDROID_HOMEorANDROID_SDK_ROOT, point to the SDK directory and are no longer needed. Open the relevant file in a text editor and delete the lines defining these variables.Save the file and then either restart your terminal or source the file to apply the changes.
Deleting Android Virtual Device (AVD) Configurations and Emulator Files
Android Virtual Devices (AVDs) are crucial for testing your apps on various devices. When you uninstall Android Studio, you’ll also want to remove any AVD configurations and emulator files to free up space and ensure a clean environment. Think of it as clearing out your virtual garage of test vehicles.Here’s how to remove AVD configurations and emulator files:
- Locate the AVD directory. AVD configurations are stored in the
.android/avddirectory within your user’s home directory. This is a hidden directory, so you may need to enable the display of hidden files in Finder (pressCommand + Shift + .) or use the command line to navigate there. - Delete the AVD configurations. Inside the
avddirectory, you’ll find a folder for each AVD you’ve created. You can delete these folders to remove the corresponding AVD configurations. - Remove emulator files. Emulator files, such as the emulator’s system images, are stored in the
.android/avddirectory, as well as potentially in the SDK directory. Delete the emulator’s system images to remove all emulator-related files. - Clean up the emulator cache. The emulator also stores cache data. To clear this, navigate to the emulator’s cache directory (usually within the SDK directory or user’s home directory) and delete its contents. This can free up a significant amount of disk space.
Listing Installed Android SDK Platforms and Related Packages
Before deleting the Android SDK, you might want to list all the installed platforms and packages to confirm what will be removed. This allows you to verify that you’re removing everything you expect.Here’s how to list installed Android SDK platforms and related packages:
- Using the Android SDK Manager (if accessible). If you still have access to the Android SDK Manager (perhaps before the final uninstall), you can open it within Android Studio (or from the command line, depending on your setup) and view the installed platforms, build tools, and other packages. This provides a graphical overview.
- Using the command line (
sdkmanager). The command-line toolsdkmanageris a powerful tool for managing the Android SDK. Even without Android Studio installed, if you still have access to the SDK tools, you can usesdkmanager. Open your terminal and run the following command to list all installed packages:
sdkmanager --listThis command will display a list of all installed packages, including their versions and installation locations.
- Parsing the output. The output of
sdkmanager --listwill be a detailed list of installed packages. Carefully review this list to ensure you’re aware of everything that will be removed when you delete the SDK directory.
Verifying the Uninstallation Process
Now that you’ve (hopefully!) successfully banished Android Studio from your Mac, let’s make sure it’sreally* gone. It’s like checking under the bed for monsters after you’ve already declared the room safe – better safe than sorry, right? This section Artikels how to definitively confirm that Android Studio has vacated the premises, leaving no trace of its presence.
Confirming Complete Removal
Ensuring that Android Studio and its associated components are entirely removed is crucial to prevent conflicts or issues if you decide to reinstall it later, or if you simply want a clean slate. Here’s how to perform the final check.To verify the uninstallation, you can employ a few key strategies.
- Checking the Applications Folder: The most obvious place to start is the Applications folder. Navigate there via Finder (Go > Applications). If Android Studio is still lurking, you’ll see its icon. If it’s gone, congratulations! You’ve likely succeeded in your mission.
- Verifying the Android Studio Directory: As mentioned earlier, Android Studio typically resides in the Applications folder. Double-check that the `Android Studio.app` directory, or any related files bearing the Android Studio name, have been completely removed.
- Examining the IntelliJ IDEA Configuration Directory: Since Android Studio is built on IntelliJ IDEA, configuration files might be stored in the user’s home directory. You can check for a directory named `~/Library/Application Support/JetBrains/AndroidStudio[version]` or similar. The `~` represents your home directory. If this directory still exists, it means some configuration data has not been removed. If it’s still there, you might need to manually delete it.
-Be cautious when deleting files in this directory, as they may contain important settings*. It’s advisable to back up the directory before deleting its contents.
- Checking for SDK and Emulator Data: If you opted to remove the Android SDK and emulator data during uninstallation, verify that the directories containing these components are also gone. The default location for the SDK is usually `~/Library/Android/sdk`, and emulator data is often found in `~/.android`. Confirm that these directories have been deleted to avoid future conflicts.
Now, let’s move on to using Spotlight to hunt down any lingering remnants.
Utilizing Spotlight for Residual File Search
Spotlight, macOS’s built-in search tool, is your secret weapon for finding any sneaky, hidden files that might have evaded your initial removal efforts. Think of it as a digital detective, sniffing out any traces of Android Studio that might remain.To use Spotlight effectively:
- Open Spotlight: Click the Spotlight icon (a magnifying glass) in the top-right corner of your screen, or press `Command + Spacebar`.
- Enter Search Terms: In the search bar, type in s related to Android Studio. Examples include: “Android Studio,” “Android SDK,” “IntelliJ,” or specific file names like “gradle.”
- Refine Your Search: Spotlight will present a list of results. If you see any files or folders that seem related to Android Studio, examine their location. You can right-click on a result and select “Show in Finder” to reveal its exact location.
- Review Results and Delete (if necessary): Carefully review the search results. If you find any files or folders that you believe should have been removed, and you are certain they are safe to delete, you can drag them to the Trash. Be extremely cautious when deleting system files. It’s best to err on the side of caution and avoid deleting anything you’re unsure about.
- Empty the Trash: After deleting any identified files, remember to empty your Trash to permanently remove them from your system.
Using Spotlight offers a thorough way to ensure that Android Studio is completely uninstalled.
Troubleshooting Common Uninstallation Issues
Sometimes, even with the best-laid plans, things go awry. Uninstalling Android Studio can be a straightforward process, but occasionally, you might encounter hiccups. Fear not! We’re here to help you navigate those tricky situations and get your Mac back to its pristine state. Let’s delve into some common roadblocks and how to overcome them.
Addressing Permission Errors During Uninstallation
Permission errors can be a real pain, popping up like uninvited guests at a party. They often arise because the uninstallation process needs access to specific files or directories, and your current user account might not have the necessary privileges.To tackle this, consider these steps:
- Check User Permissions: First, verify that your user account has administrator privileges. You can usually find this information in System Preferences (or System Settings on newer macOS versions) under “Users & Groups.” Your account should be marked as an “Admin.” If not, you may need to log in to an administrator account to proceed.
- Use `sudo` in Terminal: For command-line uninstallation, `sudo` is your friend. This command allows you to execute commands with elevated privileges. For example, if you’re trying to remove a directory, you might use:
sudo rm -rf /path/to/android/studio
You’ll be prompted to enter your administrator password. Be extremely careful when using `sudo`, as incorrect commands can potentially damage your system.
- Modify File Permissions (Cautiously): In some cases, you might need to adjust the permissions of specific files or directories. However, be cautious when doing this, as altering permissions incorrectly can cause problems. You can use the `chmod` command in Terminal to change file permissions. For example:
sudo chmod -R 777 /path/to/android/studio/directory
This command grants read, write, and execute permissions to all users for the specified directory and its contents. (Use this as a last resort and understand the security implications).
- Restart Your Mac: Sometimes, a simple restart can clear up permission-related issues. It allows the system to refresh its processes and resolve any lingering conflicts.
Handling Uninstallation Failures to Remove All Files
Sometimes, the uninstallation process doesn’t go as planned, and you’re left with remnants of Android Studio scattered across your hard drive. This can be frustrating, but there are ways to clean up the mess.Here’s how to handle a partial uninstallation:
- Manually Locate and Delete Remaining Files: After the initial uninstallation attempt, carefully search for any remaining Android Studio-related files and directories. Pay close attention to these locations:
- `~/Library/Application Support/Google/AndroidStudio` (Application Support files)
- `~/Library/Preferences/AndroidStudio` (Preferences files)
- `~/Library/Caches/AndroidStudio` (Cache files)
- `/Applications/Android Studio.app` (If it wasn’t removed)
- `~/AndroidStudioProjects` (If you didn’t choose to delete project files during the uninstallation)
- `~/Library/Preferences/com.google.android.studio.plist` (Preference files)
Use Finder or Terminal to navigate to these locations and delete any remaining files or folders.
- Use a Dedicated Uninstaller Tool (If Available): Some third-party uninstaller tools are designed to remove applications and their associated files thoroughly. Research and use such tools cautiously, as they can sometimes remove files you might need. Always back up your data before using any third-party uninstaller.
- Check for Hidden Files and Directories: Some files and directories might be hidden by default. To view hidden files in Finder, press `Command + Shift + .` (period). This can help you locate and remove any lingering files.
- Run Disk Utility: Sometimes, file system errors can prevent files from being removed correctly. Run Disk Utility (found in /Applications/Utilities/) to repair your disk and potentially resolve these issues.
Identifying Potential Problems with Running Background Components
Even after attempting to uninstall Android Studio, some of its components might still be running in the background. These lingering processes can prevent the uninstallation from completing successfully and can cause other issues.To identify and address running background components:
- Check Activity Monitor: The Activity Monitor (found in /Applications/Utilities/) is your go-to tool for monitoring processes. Open Activity Monitor and search for any processes related to Android Studio, the Android SDK, or the emulator. Examples might include `studio`, `emulator`, or `adb`.
- Force Quit Processes: If you find any related processes, select them in Activity Monitor and click the “X” button in the toolbar to force quit them. Be cautious when force quitting processes, as this can sometimes lead to data loss if the process was actively working on something.
- Use the `ps` and `kill` Commands in Terminal: For more advanced users, you can use the `ps` (process status) and `kill` commands in Terminal to identify and terminate processes.
ps aux | grep android
This command lists all processes containing “android” in their name. Then, use the `kill` command with the process ID (PID) to terminate the process.
kill -9 [PID]
Replace `[PID]` with the actual process ID. The `-9` flag sends a “SIGKILL” signal, which forcefully terminates the process. Use this with caution.
- Restart Your Mac: After force quitting any background processes, a restart can help ensure that all related components are fully shut down and that the uninstallation process can proceed without interference.
Alternative Approaches for Android Development on macOS: Uninstall Android Studio From Mac
So, you’ve bid adieu to Android Studio, or maybe you’re just exploring your options. The good news is, you’re not stuck with just one tool for building those brilliant Android apps. The macOS ecosystem offers a variety of alternative development environments, each with its own strengths and quirks. Let’s dive into some of the alternatives, and see if any of them are a good fit for you.
Alternative IDEs for Android Development on macOS
The landscape of Android development on macOS is diverse, offering options beyond the familiar confines of Android Studio. These alternative IDEs cater to different preferences and project needs. Here’s a rundown of some popular choices:
- IntelliJ IDEA: This is Android Studio’s parent IDE. Since Android Studio is built on IntelliJ IDEA, the core features and functionality are very similar. It offers excellent support for Kotlin and Java, as well as a robust plugin ecosystem.
- Visual Studio Code (VS Code): A lightweight, versatile code editor that has gained immense popularity. With the right extensions, VS Code can be transformed into a capable Android development environment.
- Eclipse: A long-standing IDE that was once a dominant force in Android development. While not as actively developed for Android as it once was, it still has a dedicated following and offers mature tooling.
- Xamarin (now part of .NET): Allows for cross-platform mobile development using C# and .NET. It’s a strong choice if you’re already familiar with the .NET ecosystem and want to target both Android and iOS.
- Android Development with Command Line Tools: A somewhat “old-school” but perfectly valid approach. You can use command-line tools like `gradle` and `adb` along with a text editor to build and debug your Android apps. This is especially useful for understanding the underlying build processes.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Alternative IDEs
Choosing an alternative IDE involves weighing the pros and cons. Each option presents a unique set of trade-offs, impacting development workflows and project capabilities. Understanding these differences helps in making an informed decision.
- IntelliJ IDEA:
- Advantages: Feature-rich, excellent code completion and refactoring, seamless integration with Android SDK, robust plugin support. It’s essentially Android Studio, but you get to choose the exact plugins you want.
- Disadvantages: Can be resource-intensive, steeper learning curve for beginners, some features might require paid subscriptions (depending on the specific version).
- Visual Studio Code (VS Code):
- Advantages: Lightweight and fast, highly customizable, extensive extension library, excellent support for various languages, free and open-source.
- Disadvantages: Requires more configuration and setup compared to Android Studio, can be less intuitive for Android-specific tasks, extension quality varies.
- Eclipse:
- Advantages: Mature IDE with a long history, good debugging tools, large community support.
- Disadvantages: Can feel dated compared to modern IDEs, Android support is not as actively maintained as in Android Studio, can be less user-friendly.
- Xamarin (now part of .NET):
- Advantages: Cross-platform development with C#, excellent for code reuse, strong performance.
- Disadvantages: Requires knowledge of C# and .NET, can have a steeper learning curve for those unfamiliar with the ecosystem, licensing costs may apply.
- Android Development with Command Line Tools:
- Advantages: Offers maximum control, understanding of the build process, can be very fast and lightweight.
- Disadvantages: Requires a good understanding of build systems and command-line tools, can be more time-consuming for complex projects, less visual debugging.
Comparison of Android Studio with Other Development Environments
The choice of IDE depends on project requirements, personal preferences, and the team’s skillset. This table compares Android Studio with other development environments based on several key criteria.
| Feature | Android Studio | IntelliJ IDEA | Visual Studio Code | Eclipse | Xamarin (.NET) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language Support | Java, Kotlin, C/C++ (NDK) | Java, Kotlin, C/C++ (NDK), and others | Java, Kotlin (with extensions), and many others | Java, C/C++ | C# |
| Ease of Use (Beginner) | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate (requires setup) | Moderate | Moderate (requires C# knowledge) |
| Performance | Good (can be resource-intensive) | Good (can be resource-intensive) | Excellent (lightweight) | Good | Good |
| Cross-Platform Development | Limited (with Flutter or other frameworks) | Limited (with Flutter or other frameworks) | Limited (with frameworks like Flutter) | Limited (with frameworks like Flutter) | Yes (Android, iOS, Windows, macOS) |
| Plugin/Extension Support | Extensive | Extensive | Very Extensive | Moderate | Moderate |
| Community Support | Very Strong | Very Strong | Very Strong | Strong | Strong |
Reinstalling Android Studio
After completely removing Android Studio from your macOS system, you might find yourself in the position of needing to reinstall it. Whether it’s to start fresh, resolve some pesky issues, or just because you fancy a change, this section will guide you through the process of getting Android Studio back up and running, along with some best practices to keep it that way.
Steps to Reinstall Android Studio on macOS
Reinstalling Android Studio on macOS is a straightforward process. Here’s how to do it, broken down into manageable steps:
- Download Android Studio: Head over to the official Android Studio download page ([https://developer.android.com/studio](https://developer.android.com/studio)). Grab the latest version specifically for macOS. It usually comes as a DMG file.
- Mount the DMG File: Once the download is complete, double-click the DMG file. This will “mount” the disk image, essentially making its contents accessible. You’ll likely see a window pop up with the Android Studio icon and a link to your Applications folder.
- Drag and Drop: Drag the Android Studio icon into your Applications folder. This copies the Android Studio application to your system.
- Eject the DMG: After the copy is complete, eject the DMG file. You can usually do this by right-clicking the mounted disk image on your desktop or in Finder and selecting “Eject.”
- Launch Android Studio: Open your Applications folder (usually by going to Finder > Applications) and double-click the Android Studio icon. The first time you launch it, macOS will likely ask if you’re sure you want to open it, as it’s a downloaded application. Click “Open.”
- Follow the Setup Wizard: Android Studio will then launch its setup wizard. This guides you through the initial configuration, including:
- Import Settings: You can choose to import settings from a previous installation (if you have them) or start fresh.
- Installation Type: Select the type of installation you want (Standard or Custom). The Standard option is usually recommended for most users.
- UI Theme: Choose your preferred UI theme (Light or Dark).
- SDK Components: Android Studio will download and install the necessary SDK components, including the Android SDK, build tools, and emulator. This might take a while, depending on your internet connection.
- Accept Licenses: During the SDK component installation, you’ll be prompted to accept various licenses. Make sure to read and accept all of them.
- Finish Setup: Once the installation is complete, you’ll be ready to start developing Android apps!
Procedure for Configuring the Development Environment After Reinstalling
After reinstalling Android Studio, the real fun begins: configuring your development environment. This involves setting up your SDK, emulators, and other tools to match your project needs.
- SDK Manager Configuration: Access the SDK Manager (Tools > SDK Manager). Here, you can:
- Install SDK Platforms: Select and install the Android SDK platforms that you’ll be targeting for your apps (e.g., Android 13, Android 14).
- Install SDK Tools: Ensure you have the necessary SDK tools installed, such as the Android SDK Build-Tools, Android Emulator, and Android SDK Platform-Tools.
- Update SDK Components: Regularly check for updates to keep your SDK components current.
- Emulator Setup:
- Create Virtual Devices: Use the AVD Manager (Tools > AVD Manager) to create virtual devices (emulators) that simulate different Android devices.
- Configure Device Settings: Customize your emulators by selecting device hardware profiles (e.g., Pixel 7, Galaxy S23), system images, and other settings. Consider allocating more RAM to the emulator for smoother performance.
- Gradle Sync: After setting up your SDK and emulators, sync your project with Gradle (File > Sync Project with Gradle Files). This ensures that your project dependencies are properly resolved.
- Build Variants: Configure your build variants to handle different build configurations (e.g., debug, release).
- Code Style and Formatting: Configure code style and formatting preferences to maintain consistency in your code. You can find these settings under File > Settings > Editor > Code Style.
- Plugins: Install any necessary plugins to enhance your development experience (e.g., Kotlin plugin, Android Lint). You can find plugins under File > Settings > Plugins.
Best Practices for Maintaining an Updated Android Studio Installation
Keeping your Android Studio installation up-to-date is crucial for performance, security, and access to the latest features. Here are some best practices to follow:
- Regularly Update Android Studio: Check for updates regularly (Help > Check for Updates). Update to the latest stable version of Android Studio as soon as it’s released.
- Keep SDK Components Updated: Use the SDK Manager to update your SDK platforms, build tools, and other components.
- Monitor Dependencies: Regularly update your project dependencies in your `build.gradle` files. These dependencies can include libraries and other components used in your projects.
- Use the Latest Gradle Version: Update the Gradle version in your project to take advantage of the latest features and performance improvements. You can usually find the latest recommended Gradle version in the Android Studio documentation or the project’s documentation.
- Clean and Rebuild Projects: Periodically clean and rebuild your projects (Build > Clean Project, then Build > Rebuild Project) to resolve potential build issues and ensure your project is up-to-date.
- Stay Informed: Subscribe to the Android Developers Blog and other official Android resources to stay informed about the latest updates, features, and best practices.
- Back Up Your Settings: Periodically back up your Android Studio settings (File > Manage IDE Settings > Export Settings) so you can easily restore them in case of a problem or when setting up a new installation.
- Manage Disk Space: Keep an eye on the disk space used by your Android Studio installation, especially the SDK and emulator data. Consider removing unused SDK platforms or emulator images to free up space.
- Utilize Version Control: Use a version control system (like Git) for your Android projects. This will help you track changes, revert to previous versions, and collaborate with other developers.
