Ip configuration failure android – Have you ever stared at your Android device, desperately willing it to connect, only to be met with the dreaded “IP configuration failure”? It’s a digital hiccup that can turn a smooth online experience into a frustrating standstill. But fear not, for this is a journey into the heart of your Android’s network connection, a tale of addresses, gateways, and the silent struggle for data access.
We’ll delve into the fundamental building blocks of your device’s digital communication, demystifying the cryptic language of IP addresses, DNS servers, and the role of DHCP in your everyday browsing.
This isn’t just a technical guide; it’s a detective story where we’ll unravel the mysteries behind those connection issues. We’ll explore the common suspects, from Wi-Fi password missteps to network congestion, and even those pesky IP address conflicts that can cause digital standoffs. Whether you’re a tech novice or a seasoned user, prepare to equip yourself with the knowledge to conquer those connectivity challenges and regain control of your digital life.
We’ll examine both Wi-Fi and mobile data issues, providing step-by-step solutions, and even explore the advanced techniques that’ll make you the master of your Android’s network destiny.
Understanding IP Configuration Failure on Android
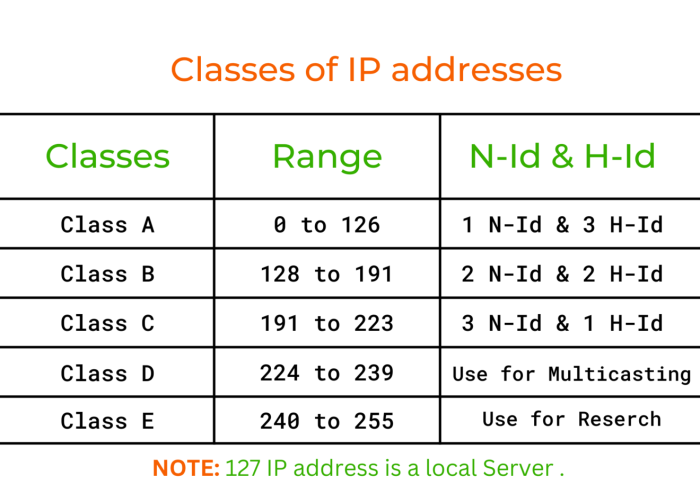
Let’s delve into the often-confusing world of IP configuration on your Android device. It’s like the secret handshake your phone uses to talk to the internet. When that handshake goes wrong, things can get frustrating. This guide breaks down the essential concepts, symptoms, and solutions in a clear, easy-to-understand manner.
Fundamental Network Concepts for Android Devices
Understanding how your Android device connects to the internet requires grasping a few key players. They work together seamlessly, usually, to get you online.
- IP Addresses: Think of an IP address as your phone’s unique postal code on the internet. It’s a numerical label assigned to every device connected to a network, allowing data to be sent and received. It’s like your street address; without it, the internet doesn’t know where to send information. There are two main types: IPv4 (e.g., 192.168.1.100) and IPv6 (a much longer address, designed to accommodate the growing number of internet-connected devices).
- Gateways: The gateway is the “front door” of your network. It’s the device (usually your router) that connects your local network (your home Wi-Fi) to the wider internet. All internet traffic from your phone passes through the gateway. Imagine it as the guard at the entrance of a building, directing traffic in and out.
- DNS Servers: DNS (Domain Name System) servers are like the phonebook of the internet. They translate human-readable domain names (like google.com) into IP addresses that computers understand. Without DNS, you’d have to remember a long string of numbers to visit your favorite websites. When you type “google.com” in your browser, your phone asks a DNS server for the corresponding IP address.
- DHCP: DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is the automated system that assigns IP addresses, gateway addresses, DNS server addresses, and other network settings to your device. It’s a convenience, preventing you from manually configuring all these settings every time you connect to a new Wi-Fi network. DHCP is often enabled by default on your router.
Defining “IP Configuration Failure” on Android
An IP configuration failure on your Android device essentially means your phone can’t successfully obtain or maintain the network settings it needs to connect to the internet. This could be due to a variety of reasons, ranging from incorrect network settings to issues with the router itself. It’s the digital equivalent of being locked out of your own house.
Common Symptoms of IP Configuration Issues
When your Android device experiences IP configuration problems, you’ll likely encounter a few telltale signs.
- “No internet connection” or “Connected, but no internet”: This is the most common symptom. Your phone might show it’s connected to Wi-Fi, but you can’t browse the web, use apps that require internet, or send emails. It’s like having a phone line that’s connected but doesn’t have a dial tone.
- Unable to obtain an IP address: Your phone might continuously try to connect to a Wi-Fi network, but it fails to get an IP address from the router. The device will typically display a message such as “Obtaining IP address…” and never proceed further.
- Slow internet speeds: Even if you’re connected, your internet speed might be drastically reduced. This could be due to a variety of factors, including IP configuration issues, but it’s often a symptom of underlying network problems.
- Intermittent connectivity: Your phone might connect and disconnect from the network repeatedly. This can be extremely frustrating, as you might lose your connection mid-browsing or while using an app.
Static vs. Dynamic IP Configuration on Android
Android devices can be configured to use either a static or dynamic IP address. Understanding the difference is crucial for troubleshooting IP configuration failures.
- Dynamic IP: This is the default setting. Your device automatically obtains its IP address and other network settings from the DHCP server (usually your router). This is generally the easiest and most convenient option.
- Static IP: In a static IP configuration, you manually enter the IP address, gateway, DNS server addresses, and other network settings. This is less common but can be useful in certain situations, such as when you need to assign a fixed IP address to your device for network management or remote access. It’s like having a permanent parking spot; the address never changes.
Common Causes of IP Configuration Failure: Ip Configuration Failure Android
Sometimes, your Android device just won’t connect to the internet, and the dreaded “IP configuration failure” message pops up. It’s frustrating, we get it! But understanding the common culprits behind this issue is the first step toward getting back online. Let’s delve into the usual suspects.
Incorrect Wi-Fi Passwords
The most frequent cause of IP configuration failure stems from a simple, yet easily overlooked, problem: an incorrect Wi-Fi password.Imagine trying to enter a secret club without the password; you simply won’t get in. Similarly, your Android device requires the correct password to join a Wi-Fi network and obtain an IP address. Even a single misplaced character can prevent a successful connection.
Double-check every character, paying close attention to capitalization and special symbols. It’s easy to mistype a “0” for an “O” or a “1” for an “l”.
Network Congestion or Overloaded Routers
Network congestion, akin to rush hour on a busy highway, can significantly impede your device’s ability to obtain an IP address.Think of your router as the traffic controller. If too many devices are simultaneously requesting an IP address, the router becomes overloaded, leading to delays and potential failures. This is particularly noticeable during peak hours when many people are online.
The router’s processing power and bandwidth are finite resources. Imagine a restaurant during a popular event: too many customers, and service slows down considerably. If the router’s resources are exhausted, IP address assignment may fail entirely.
Conflicting IP Addresses
IP address conflicts are another common source of frustration, like two people claiming the same seat on a train.If two devices on the same network attempt to use the same IP address, a conflict arises, and one or both devices will fail to connect. This often happens when static IP addresses are configured manually. For example, if you manually assigned your laptop the IP address 192.168.1.100, and then your Android device tries to obtain the same address through DHCP, a conflict will occur.
The router detects the duplication and prevents the Android device from successfully obtaining an IP address. The router attempts to prevent these conflicts by checking if the address is already in use before assigning it.
DHCP Server Issues
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server is the unsung hero of your network, responsible for automatically assigning IP addresses. When this server malfunctions, connectivity problems arise. Here are some potential issues:The DHCP server, often embedded within your router, hands out IP addresses, gateway addresses, DNS server addresses, and other network configuration parameters to all devices connecting to your network.
- DHCP Server Down: If the DHCP server itself is down or experiencing problems, it cannot distribute IP addresses. This is akin to the postal service shutting down, no mail will be delivered.
- IP Address Pool Exhaustion: The DHCP server has a limited pool of IP addresses it can assign. If all addresses are in use, new devices won’t be able to connect. Think of a hotel with no vacancies.
- Incorrect DHCP Server Configuration: Misconfigured settings within the DHCP server can prevent it from assigning valid IP addresses. This could include incorrect subnet masks or gateway addresses.
- DHCP Lease Time Issues: DHCP leases are temporary assignments of IP addresses. If the lease time is too short, devices may frequently lose their IP addresses and need to re-request them, potentially causing connection interruptions. Conversely, if the lease time is too long, the DHCP server may not be able to assign new addresses to new devices.
- Router Firmware Problems: Outdated or corrupted router firmware can sometimes cause the DHCP server to malfunction.
Troubleshooting Steps
?w=700)
Dealing with Wi-Fi woes on your Android device can be frustrating. Thankfully, a few straightforward steps often resolve connectivity issues. Let’s delve into a practical guide to get you back online.
Wi-Fi Issues
Sometimes, the simplest solutions are the most effective. Before you tear your hair out, try these basic troubleshooting steps.
- Restart Your Device: A classic for a reason! A simple restart clears temporary glitches that might be causing the problem.
- Check Airplane Mode: Make sure Airplane Mode is off. It disables all wireless connections, including Wi-Fi.
- Verify Wi-Fi is Enabled: Ensure Wi-Fi is toggled on in your device’s settings.
- Move Closer to the Router: Physical obstructions and distance can weaken the signal. Move closer to the router to see if that helps.
Forgetting and Reconnecting to a Wi-Fi Network
Sometimes, the stored network settings become corrupted. Forgetting and reconnecting can refresh the connection and resolve the issue.
- Navigate to Wi-Fi Settings: Open your Android device’s settings and tap on “Wi-Fi.”
- Select the Network: Locate the problematic Wi-Fi network in the list of available networks.
- Forget the Network: Tap and hold on the network name. A menu should appear with an option to “Forget” or “Remove.” Select this option.
- Reconnect: Tap on the network name again. You will be prompted to enter the Wi-Fi password. Enter the password and tap “Connect.”
Checking and Resetting Router Configuration
The router itself can be the culprit. Checking its settings and, if necessary, resetting it can often solve the problem. This is a bit more involved, so proceed with care.
- Access Router Configuration: You’ll typically need to access your router’s configuration page through a web browser. The default IP address is often something like 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1. Check your router’s manual for the specific address.
- Log In: You’ll need the router’s username and password. These are often printed on the router itself or in the manual.
- Check Internet Connection: Once logged in, look for a status page or a section that displays the internet connection status. Ensure the router is connected to the internet.
- Restart the Router: Look for a “Reboot” or “Restart” option in the router’s settings. This is a common first step to try.
- Reset to Factory Defaults (Last Resort): If all else fails, you can reset the router to its factory default settings. Be aware that this will erase all custom configurations, including your Wi-Fi password. You’ll need to set up the Wi-Fi network again. There is usually a small reset button on the back of the router that you hold down for several seconds.
Checking Signal Strength and Interference
A weak Wi-Fi signal or interference from other devices can lead to connectivity problems. Here’s how to check.
- Check Signal Strength on Your Device: Look for the Wi-Fi icon in the status bar. The number of bars indicates the signal strength. Fewer bars mean a weaker signal.
- Use a Wi-Fi Analyzer App: Download a Wi-Fi analyzer app from the Google Play Store. These apps scan the area for Wi-Fi networks and display signal strength, channel usage, and interference levels.
- Identify Interference: The analyzer app can show you which channels are congested. If your router is using a crowded channel, try changing it in the router’s settings. Common sources of interference include microwave ovens, Bluetooth devices, and other Wi-Fi networks.
- Change the Router Channel: Access your router’s settings and look for a Wi-Fi channel setting. Experiment with different channels to find one with less interference. Channels 1, 6, and 11 are often recommended because they don’t overlap as much.
Troubleshooting Steps for Different Wi-Fi Security Protocols
Different Wi-Fi security protocols have varying levels of security and compatibility. Here’s a comparison of troubleshooting steps, taking into account the different security types:
| Security Protocol | Common Issues | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|
| WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) |
|
|
| WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) |
|
|
| WPA2/3 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2/3) |
|
|
Troubleshooting Steps
Dealing with mobile data woes on your Android device can feel like navigating a digital maze. But fear not! This section provides a practical guide to diagnosing and fixing cellular connectivity problems, ensuring you stay connected to the digital world. Let’s delve into the troubleshooting steps, transforming frustration into fluency.
Mobile Data Issues
Mobile data connectivity problems can manifest in several ways: slow browsing speeds, intermittent connection drops, or a complete inability to access the internet. These issues can stem from various sources, but thankfully, most are readily solvable with the right approach. Let’s break down the process.
- Checking APN Settings: Access Point Names (APNs) are essentially the gateways your phone uses to connect to your mobile carrier’s network. Incorrect APN settings can prevent your device from establishing a data connection.
To verify and, if necessary, correct your APN settings, follow these steps:
- Navigate to your Android device’s settings. This can usually be done by tapping the “Settings” icon, which often resembles a gear or cogwheel.
- Locate the “Connections” or “Network & Internet” section. The exact wording might vary depending on your device manufacturer and Android version.
- Select “Mobile Networks” or “Mobile Data”.
- Choose “Access Point Names” (APNs). This is where the magic happens.
- Compare your current APN settings to the ones provided by your mobile carrier. You can usually find these settings on your carrier’s website or by contacting their customer support.
- If the settings don’t match, you’ll need to edit the existing APN or create a new one with the correct information. Be meticulous; even a single incorrect character can disrupt the connection. The crucial fields to double-check include the APN name, the username, the password, and the authentication type.
- Once you’ve entered the correct APN settings, save the changes and restart your device. This often helps to refresh the connection and apply the new settings.
Incorrect APN settings are a common culprit behind mobile data failures. Correcting these settings is often the first and most effective step in resolving connectivity issues.
- Toggling Airplane Mode: Airplane mode is a simple yet effective tool for resetting your device’s network connections. When enabled, Airplane mode disables all wireless communications, including cellular data, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth.
Here’s how to use Airplane mode to troubleshoot your mobile data:
- Access the Quick Settings panel by swiping down from the top of your screen.
- Locate the Airplane mode icon, which typically resembles an airplane.
- Tap the icon to enable Airplane mode. Wait a few seconds to allow the device to fully disconnect.
- Tap the Airplane mode icon again to disable it. This will reactivate your device’s wireless radios and attempt to reconnect to the mobile network.
- Test your mobile data connection. If it’s working, great! If not, proceed to the next troubleshooting steps.
Toggling Airplane mode is like giving your device a quick “reboot” for its network connections. It’s a fast and easy first step to try.
- Resetting Network Settings: Resetting network settings is a more drastic measure, but it can resolve persistent connectivity issues by clearing all saved Wi-Fi passwords, Bluetooth connections, and APN settings, effectively restoring them to their default configurations.
To reset your network settings:
- Go to your device’s Settings.
- Tap on “General Management” or “System”.
- Select “Reset”.
- Choose “Reset network settings”.
- Confirm your choice, and the device will restart after the reset process is complete.
Be aware that resetting network settings will erase all your saved Wi-Fi passwords and Bluetooth pairings, so you’ll need to reconnect to these devices manually.
- Verifying Data Roaming Settings: If you’re traveling outside your home network, data roaming settings are critical. Data roaming allows your device to connect to a mobile network in a foreign country or region.
To ensure your data roaming settings are configured correctly:
- Go to Settings, then “Connections” or “Network & Internet”.
- Select “Mobile Networks” or “Mobile Data”.
- Find the “Data roaming” option and ensure it’s enabled. You might need to select “Roaming” or a similar option.
- Check your mobile carrier’s policy regarding data roaming charges. Roaming can incur additional costs, so it’s essential to understand the associated fees.
- If you’re unsure about the roaming charges, contact your mobile carrier to clarify the costs. Consider disabling data roaming if you want to avoid these charges, but be aware that you will not be able to use mobile data.
Data roaming is essential for staying connected when you travel, but it’s important to be aware of the potential costs involved.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
Sometimes, the basic troubleshooting steps just aren’t enough to get your Android device connected to the network. When you’re facing persistent IP configuration woes, it’s time to delve into the more advanced techniques. These methods provide a deeper level of control and allow for more targeted diagnostics, ultimately leading to a more robust and reliable network connection.
Manually Configuring a Static IP Address
Manually assigning a static IP address can sometimes bypass issues caused by a malfunctioning DHCP server or a conflict with other devices on the network. This involves directly configuring the network settings on your Android device.To manually configure a static IP address, follow these steps:
- Navigate to your device’s Wi-Fi settings. This is usually found under “Settings” and then “Network & Internet” or a similar heading, depending on your Android version.
- Select the Wi-Fi network you’re connected to.
- Long-press (or tap on the network name) to access advanced options. You may need to tap the gear icon or a similar icon to view more details.
- Look for an option labeled “IP settings” or something similar.
- Change the IP settings from “DHCP” (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) to “Static”.
- Enter the following information:
- IP Address: A unique IP address within your network’s range. This address must not be in use by any other device. You can typically find your network’s IP range by looking at the router’s configuration or by checking the IP address of another connected device. For example, if your router assigns addresses in the range of 192.168.1.100 to 192.168.1.200, you could choose an address like 192.168.1.150, but it is important to first check if this IP is not being used by other devices.
- Gateway: This is typically the IP address of your router. It’s usually something like 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1.
- Network prefix length: This specifies the subnet mask in CIDR notation. A common value is 24, which corresponds to a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
- DNS 1 and DNS 2: These are the addresses of your DNS servers. You can use your ISP’s DNS servers or public DNS servers like Google’s (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare’s (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1).
- Save the settings.
- Test your connection by opening a web browser and trying to access a website.
Using Network Diagnostic Tools (Ping)
The “ping” command is a fundamental network diagnostic tool that helps determine if your device can communicate with other devices on the network and the internet. It sends small packets of data to a target and measures the time it takes to receive a response.Here’s how to use the “ping” command and other diagnostic tools:
- Ping: While Android doesn’t have a built-in “ping” command in its standard terminal, you can download a terminal emulator app from the Google Play Store (e.g., Termux). Once installed, open the app and type the following:
ping [IP address or domain name]. For example, to ping Google’s DNS server, you would typeping 8.8.8.8. The output will show you the round-trip time (RTT) for each packet and whether the packets are being received.High RTTs or packet loss indicate network issues.
- Traceroute (or Tracert): This command traces the route a packet takes to reach a destination, showing each hop (router) along the way. Similar to ping, you might need a terminal emulator app. The command is usually
traceroute [IP address or domain name]. This can help identify where a connection is failing. - Network Speed Test Apps: Apps like Speedtest by Ookla can measure your download and upload speeds, providing insights into your internet connection’s performance. This can help determine if the IP configuration issues are causing slow speeds.
- Network Analyzer Apps: These apps offer a range of diagnostic tools, including port scanning, DNS lookup, and Wi-Fi signal analysis, providing a comprehensive view of your network environment.
Clearing Cache and Data of Network-Related Apps
Sometimes, corrupted data within network-related apps can cause IP configuration problems. Clearing the cache and data of these apps can often resolve these issues.Here’s how to clear the cache and data of network-related apps:
- Go to “Settings” on your Android device.
- Tap on “Apps” or “Apps & Notifications” (the exact wording may vary depending on your Android version).
- Find and tap on the following apps:
- Wi-Fi: This may be listed as “Wi-Fi” or “Wireless”.
- Network Services: Look for apps with names related to network management.
- Your Browser(s): The browser you use most often to access the internet.
- Tap on “Storage & cache”.
- Tap “Clear cache”. If the problem persists, tap “Clear storage” or “Clear data”. This will reset the app to its default state, so you may need to re-enter any saved settings. Be aware that clearing data will erase any saved data.
- Restart your device after clearing the cache and data.
Static IP vs. DHCP: Benefits and Drawbacks
Understanding the differences between static and dynamic IP addressing is crucial for effective troubleshooting. The following table provides a clear comparison.
| Feature | Static IP | DHCP (Dynamic IP) |
|---|---|---|
| Configuration | Manually configured; requires knowledge of network settings. | Automatically configured by the DHCP server (usually the router). |
| Address Stability | IP address remains constant unless manually changed. | IP address can change over time, typically through a lease system. |
| Management | Requires more manual administration; suitable for devices needing a fixed IP. | Easier to manage, especially in large networks; less manual intervention. |
| Conflict Potential | Risk of IP address conflicts if the same address is assigned to multiple devices. | Lower risk of IP conflicts, as the DHCP server manages address allocation. |
| Security | Can be slightly more secure if used in conjunction with other security measures, such as IP address filtering on the router. | Security is dependent on the router’s security settings. |
| Use Cases | Servers, printers, and devices that need a consistent IP address for remote access or network services. | Most home and small business networks, where ease of use and automatic configuration are preferred. |
Visual Representation of the IP Configuration Process
The process of IP configuration can be visualized as a journey from your device to the internet.Imagine your Android device as a traveler setting out on a journey.
1. The Device (Traveler): The journey begins on your Android device. It initiates a request to join the network.
2. The Router (The Gateway): Your device sends a request to the router, which acts as the gateway to the internet. The router has a DHCP server (a travel agent) that assigns a unique IP address to your device, along with other network information (like the subnet mask and DNS servers).
3. The Internet (The Destination): Once the device has an IP address, it can communicate with the internet. The router forwards your device’s requests to the internet. Data travels between your device and the internet through the router.
4. The DNS Server (The Navigator): The DNS server translates domain names (like google.com) into IP addresses, allowing your device to find the servers it needs to access websites. This is like using a map to find your way.
5. Data Flow (The Journey): When you browse the web, your device sends requests to websites. The router and DNS servers help guide these requests and the responses back to your device.
Router-Specific Solutions

Let’s face it, your router is the unsung hero of your digital life. It’s the gatekeeper, the traffic controller, and sometimes, the source of all your network woes. When your Android device is struggling with IP configuration, the router is often the prime suspect. This section dives deep into the router’s role in this digital drama, offering solutions to get your connection back on track.
We’ll explore how to wrangle your router’s settings, check its vital signs, and give it a good ol’ reboot – all in the name of a stable IP address.
Accessing and Managing the Router’s Configuration Interface
Your router’s configuration interface is like the cockpit of an airplane. It’s where you control everything, from the Wi-Fi password to the DHCP settings. Gaining access is the first step in diagnosing and fixing IP configuration problems.To access the configuration interface:
- Identify the Router’s IP Address: This is usually the gateway address for your network. You can often find this in your Android device’s Wi-Fi settings. Look for “Gateway” or “Router” under the network details. Alternatively, check your computer’s network settings (e.g., in Windows, use `ipconfig` in the command prompt; on macOS/Linux, use `ifconfig` or `ip addr`). Common default gateway addresses include 192.168.1.1, 192.168.0.1, and 10.0.0.1.
- Open a Web Browser: On your computer or any device connected to your network, open a web browser (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, etc.).
- Enter the IP Address: In the address bar, type the router’s IP address and press Enter.
- Log In: You’ll be prompted for a username and password. These are usually found on a sticker on the router itself or in the router’s documentation. Common default credentials include “admin” for both username and password, or variations like “admin” with a blank password. Be aware of the security risks of using default credentials; change them after you log in!
- Navigate the Interface: Once logged in, you’ll see the router’s configuration interface. The layout varies depending on the router’s manufacturer, but you’ll typically find options for Wi-Fi settings, DHCP settings, firewall settings, and firmware updates.
Remember, changing settings incorrectly can disrupt your network. Always proceed with caution and consult your router’s manual if you’re unsure about a particular setting.
Checking the DHCP Server Settings on the Router
The DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server is the part of your router that hands out IP addresses to devices on your network. If the DHCP server is misconfigured, your Android device might fail to obtain a valid IP address. Checking these settings is crucial.Here’s how to check DHCP server settings:
- Access the Router’s Configuration Interface: Follow the steps Artikeld in the previous section to log in to your router.
- Locate the DHCP Settings: The location of the DHCP settings varies, but they’re usually found under “LAN Settings,” “Network Settings,” or a similar category. Look for a section related to DHCP or IP address allocation.
- Verify the DHCP Server is Enabled: Ensure that the DHCP server is enabled. There should be a checkbox or toggle switch to enable or disable it. If it’s disabled, your devices won’t automatically receive IP addresses.
- Check the IP Address Range: The DHCP server assigns IP addresses from a defined range. Make sure this range is appropriate for your network. A typical range might be 192.168.1.100 to 192.168.1.200. Ensure the range is large enough to accommodate all your devices.
- Verify the Lease Time: The lease time determines how long a device keeps its assigned IP address. A shorter lease time (e.g., a few hours) might lead to frequent IP address renewals, while a very long lease time (e.g., several days) might cause conflicts if many devices connect and disconnect frequently. A default lease time of 24 hours is usually a good starting point.
If you find any issues with these settings, adjust them accordingly. Save the changes and restart your router for the new settings to take effect. If you have a large network with many devices, consider increasing the IP address range.
Rebooting the Router and Its Impact on IP Configuration Issues
Sometimes, the simplest solution is the most effective. Rebooting your router is like giving it a digital reset button. It clears the temporary memory, reloads the configuration, and can often resolve IP configuration problems.Here’s why rebooting works and how to do it:
- Why Rebooting Works: Routers, like any computer, can experience software glitches or temporary errors. Rebooting clears these errors and restarts the router’s processes. This can fix issues with the DHCP server, DNS resolution, and other network functions.
- How to Reboot the Router: There are several ways to reboot your router:
- Via the Configuration Interface: Many routers have a “Reboot” or “Restart” button within their configuration interface. Simply navigate to the appropriate section and click the button.
- Using the Power Button: Most routers have a power button. Press the power button to turn off the router. Wait about 30 seconds, then press the power button again to turn it back on.
- Unplugging and Plugging: The most common method is to unplug the router from the power outlet. Wait about 30 seconds, then plug it back in.
- Impact on IP Configuration: Rebooting the router forces all connected devices to request a new IP address from the DHCP server. This can resolve conflicts and ensure that your Android device receives a valid IP address.
After rebooting, allow the router a few minutes to fully restart before attempting to connect your Android device.
Updating the Router’s Firmware to Resolve Network Problems
Router firmware is the software that runs on your router. Just like your phone or computer, routers need updates to fix bugs, improve performance, and enhance security. Updating the firmware can often resolve IP configuration issues and other network problems.Here’s how to update your router’s firmware:
- Access the Router’s Configuration Interface: Log in to your router’s configuration interface as described earlier.
- Locate the Firmware Update Section: The location of the firmware update section varies, but it’s usually found under “Administration,” “Maintenance,” or “Firmware Update.”
- Check for Updates: The router will typically have an option to check for available updates. Click the “Check for Updates” button.
- Download and Install the Update: If an update is available, follow the on-screen instructions to download and install it. This process usually involves downloading the update file and then uploading it to the router.
- Wait for the Update to Complete: The update process can take several minutes. Do not interrupt the process by turning off the router or disconnecting it from the power source. The router will usually reboot automatically after the update is complete.
It is important to note:
Always back up your router’s configuration settings before updating the firmware. This allows you to restore your settings if something goes wrong during the update.
Firmware updates can sometimes introduce new problems, so it’s a good idea to research the update and see if other users have reported any issues before proceeding.
Identifying and Resolving Potential Issues with the Router’s Firewall Settings
The router’s firewall is designed to protect your network from external threats. However, overly restrictive firewall settings can sometimes interfere with your Android device’s ability to obtain an IP address or access the internet.Here’s how to identify and resolve potential firewall issues:
- Access the Router’s Configuration Interface: Log in to your router’s configuration interface.
- Locate the Firewall Settings: The firewall settings are usually found under “Firewall,” “Security,” or a similar category.
- Check the Firewall Level: Some routers offer different firewall levels (e.g., low, medium, high). If the firewall level is set too high, it might block legitimate network traffic. Try lowering the firewall level to see if it resolves the issue.
- Review Port Filtering Rules: The firewall might have rules that block specific ports. Your Android device needs to use certain ports to communicate with the internet. Make sure that the necessary ports are not blocked. Common ports include 80 (HTTP), 443 (HTTPS), and others used by various apps and services.
- Check for MAC Address Filtering: Some routers allow you to filter network access based on the MAC address of a device. Make sure that your Android device’s MAC address is not blocked.
- Temporarily Disable the Firewall: As a troubleshooting step, you can temporarily disable the firewall to see if it resolves the IP configuration issue. If disabling the firewall fixes the problem, you know the firewall is the culprit. Re-enable the firewall and then adjust the settings to allow the necessary traffic.
Proceed with caution when adjusting firewall settings. Incorrect settings can leave your network vulnerable to security threats. If you’re unsure about a particular setting, consult your router’s manual or seek assistance from a network professional.
Preventing Future IP Configuration Failures
Let’s face it, nobody enjoys wrestling with their phone to get online. The good news is, by taking some proactive steps, you can significantly reduce the chances of encountering those frustrating IP configuration errors in the future. Think of it like preventative medicine for your network – a little care now can save you a lot of headaches later.
Maintaining a Stable and Reliable Network Connection, Ip configuration failure android
A consistently stable network is the bedrock of smooth online experiences. It’s the difference between a seamless video call and a pixelated, stuttering mess. Maintaining a stable connection is not rocket science; it involves a few key practices that ensure your devices can readily communicate with the internet.
- Regularly Check Your Router’s Physical Connections: Ensure all cables (Ethernet, power) are securely plugged in. A loose cable can cause intermittent connectivity issues, leading to IP failures. It’s like checking the tires before a road trip – a simple inspection can prevent a major breakdown.
- Position Your Router Strategically: Place your router in a central location, away from obstructions like walls, metal objects, and other electronic devices. These can interfere with the Wi-Fi signal. Consider it the sun in your home network ecosystem; it needs to shine unobstructed.
- Monitor Network Traffic: Keep an eye on your network usage. Excessive bandwidth consumption can lead to congestion and connection problems. Many routers have built-in monitoring tools. Think of it as knowing when to ease off the gas pedal to prevent a traffic jam.
- Avoid Network Overload: Limit the number of devices simultaneously connected to your network, especially during peak usage times. This helps to prevent the network from becoming overwhelmed.
The Importance of Regularly Updating Android Devices and Router Firmware
Keeping your Android device and router firmware updated is akin to giving your gadgets a regular checkup. These updates often contain crucial security patches, performance improvements, and bug fixes that are vital for maintaining a healthy and efficient network environment.
Android Device Updates: Android updates frequently include security patches that address vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors. They also often optimize network protocols, which can improve IP address acquisition and overall connection stability. For instance, a 2023 study by Google found that devices running older versions of Android were significantly more susceptible to malware attacks compared to those running the latest updates.
This emphasizes the importance of keeping your device up to date to minimize security risks.
Router Firmware Updates: Router firmware updates similarly provide security enhancements and performance boosts. Manufacturers regularly release updates to address known security flaws, improve Wi-Fi signal strength, and optimize network handling. Neglecting these updates can leave your network vulnerable to attacks and potentially lead to IP configuration problems due to outdated protocols or known bugs. A recent report by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) highlighted the prevalence of routers as entry points for cyberattacks, underscoring the necessity of timely firmware updates.
Best Practices for Securing a Wi-Fi Network to Prevent Unauthorized Access
Securing your Wi-Fi network is like locking your front door. It prevents unwanted guests from entering and potentially causing trouble. A well-secured network not only protects your personal data but also contributes to a more stable and reliable connection. Unauthorized access can hog bandwidth, slow down your network, and even lead to IP configuration conflicts.
- Use a Strong Password: Choose a strong, complex password for your Wi-Fi network. Avoid using easily guessable passwords like your name, date of birth, or common words. A strong password should be at least 12 characters long and include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Enable WPA3 Encryption: WPA3 is the latest and most secure Wi-Fi security protocol. It provides stronger encryption than older protocols like WPA2 and WEP, making it significantly harder for unauthorized users to access your network. Check your router’s settings to ensure WPA3 is enabled.
- Change the Default Router Password: The default password for your router is often well-known and can be easily found online. Change it immediately after setting up your router.
- Disable WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup): WPS is a feature designed to simplify connecting devices to your Wi-Fi network. However, it can be vulnerable to brute-force attacks. Disable WPS in your router’s settings to enhance security.
- Hide Your Network Name (SSID): While hiding your SSID (Service Set Identifier) doesn’t guarantee complete security, it can make it slightly more difficult for casual snoopers to find your network.
- Regularly Monitor Connected Devices: Periodically check the list of devices connected to your Wi-Fi network. If you see any unfamiliar devices, immediately change your Wi-Fi password.
- Use a Firewall: Most routers have a built-in firewall that helps protect your network from unauthorized access. Ensure your firewall is enabled.
Recommendations to Improve Network Performance and Reduce the Likelihood of IP Configuration Failures
To ensure a consistently smooth online experience, adopting practices that optimize your network’s performance is essential. These steps not only enhance speed and reliability but also directly address the underlying causes of IP configuration failures. A well-tuned network is less prone to the errors that disrupt your connectivity.
- Use a Wired Connection for High-Demand Devices: Whenever possible, connect devices that require a stable and high-bandwidth connection (like gaming consoles or desktop computers) directly to your router using an Ethernet cable. This reduces Wi-Fi congestion and improves overall network performance.
- Optimize Router Channel Settings: Wi-Fi routers operate on different channels. Choose a channel that is less congested to minimize interference. Many routers have an “auto” setting that automatically selects the best channel.
- Upgrade Your Router: If you have an older router, consider upgrading to a newer model that supports the latest Wi-Fi standards (like Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E). Newer routers offer improved performance, better range, and enhanced security features.
- Limit the Number of Connected Devices: The more devices connected to your network, the more strain is placed on its resources. If you have many devices, consider prioritizing the bandwidth allocated to critical devices or limiting the number of devices connected simultaneously.
- Use a Static IP Address: While DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is the default method for assigning IP addresses, using a static IP address for critical devices can sometimes improve stability and reduce IP configuration conflicts. This is especially helpful for devices that require a consistent IP address, such as network printers or servers.
- Periodically Reboot Your Router and Modem: Rebooting your router and modem can clear temporary files, refresh network connections, and resolve minor issues that might be causing IP configuration problems. Do this at least once a month.
- Consider a Mesh Wi-Fi System: If you have a large home or experience Wi-Fi dead zones, a mesh Wi-Fi system can provide more consistent coverage and improve network performance.
