Android os on raspberry pi 3 – Embark on an thrilling expedition into the realm of miniaturized computing! Think about the facility of Android, that acquainted and versatile working system, nestled snugly throughout the confines of a Raspberry Pi
3. Sure, you heard it proper: android os on raspberry pi 3 isn’t just a dream; it is a tangible actuality, a fusion of two technological titans. This endeavor opens up a world of prospects, from reworking your Pi into a conveyable media middle to crafting your personal sensible house hub, all whereas harnessing the immense potential of Android’s huge ecosystem.
Put together to be amazed as we unravel the secrets and techniques of this compelling mixture, exploring its intricacies, challenges, and finally, its boundless potential.
We’ll delve into the nitty-gritty, from gathering the mandatory elements – the Raspberry Pi 3 itself, a trusty microSD card, and a dependable energy supply – to navigating the often-tricky waters of software program set up. We’ll study the totally different Android OS distributions obtainable, every providing a singular taste and set of options, and offer you the instruments and data to decide on the proper one in your wants.
Moreover, we’ll information you thru the flashing course of, step-by-step, making certain a easy and profitable transition from idea to creation. Get able to unlock the total potential of your Raspberry Pi 3 and expertise Android in a complete new, compact, and customizable means.
Introduction: Android OS on Raspberry Pi 3
So, you are interested in working Android on a Raspberry Pi 3? Put together for a journey the place the cell world meets the miniature pc! It is an enchanting mix, opening up a world of prospects and some potential hiccups. This exploration will delve into the core ideas, historic context, and the sensible execs and cons of this intriguing mixture.
Idea of Operating Android OS on a Raspberry Pi 3, Android os on raspberry pi 3
The essence of working Android on a Raspberry Pi 3 boils all the way down to a intelligent adaptation. Consider it like transplanting the mind of a smartphone or pill (Android) into the physique of a credit-card-sized pc (Raspberry Pi 3). That is achieved by way of custom-built Android distributions, particularly tailor-made to the Pi’s {hardware} structure. These distributions, usually primarily based on Android Open Supply Venture (AOSP), comprise the core Android system, drivers for the Pi’s elements (like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and USB ports), and a consumer interface.
This lets you expertise the acquainted Android setting – apps, video games, and all – on a tool far faraway from its cell origins. The Pi acts because the host, executing the Android working system, enabling customers to work together with the acquainted Android interface by way of related peripherals reminiscent of a keyboard, mouse, and show.
Transient Historical past of Android and its Evolution on Totally different {Hardware} Platforms
Android’s journey has been nothing wanting spectacular. Initially conceived as a digicam working system, it was acquired by Google in 2005 and pivoted to turn out to be the powerhouse cell OS we all know right this moment. Its early days noticed it totally on smartphones, evolving quickly with every iteration. Then, it expanded to tablets, wearables, and even sensible TVs. The transfer to totally different {hardware} platforms, together with the Raspberry Pi, is a testomony to its adaptability and the open-source nature of its basis.
This has facilitated the event of {custom} builds by lovers and builders, who port the OS to numerous units.
Advantages of Utilizing Android on a Raspberry Pi 3
There’s so much to like about this pairing! Android on a Raspberry Pi 3 affords some compelling benefits.
- Value-Effectiveness: Raspberry Pi 3 boards are comparatively cheap, making them a cheap different to buying devoted Android units.
- Versatility: You possibly can repurpose an outdated monitor or TV and use it as an Android-powered media middle, digital signage, or perhaps a primary desktop pc.
- Customization: The open-source nature of Android permits for in depth customization, enabling customers to tailor the expertise to their particular wants. You possibly can set up {custom} launchers, modify system settings, and even develop your personal functions.
- Entry to the Google Play Retailer: Most Android distributions for the Pi embody entry to the Google Play Retailer, granting you entry to an enormous library of functions and video games.
- Academic Potential: It is a improbable platform for studying about embedded methods, software program improvement, and the interior workings of Android.
Drawbacks of Utilizing Android on a Raspberry Pi 3
In fact, there are trade-offs. The expertise is not all the time excellent, and it is important to pay attention to the restrictions.
- Efficiency Limitations: The Raspberry Pi 3, whereas succesful, isn’t as highly effective as trendy smartphones or tablets. Count on some lag, particularly when working demanding functions or video games.
- Software program Compatibility: Not all Android apps are assured to work flawlessly on the Pi. Some apps might crash, have show points, or lack assist for particular {hardware} options.
- Driver Assist: Driver assist for sure Raspberry Pi {hardware} elements, such because the digicam or the show’s contact capabilities, could also be restricted or require further configuration.
- Consumer Expertise: The consumer interface may not be as easy or responsive as on a devoted Android machine. You may want to regulate your expectations.
- Ongoing Growth: Whereas the group is energetic, the event of Android distributions for the Raspberry Pi 3 is ongoing, which implies that updates and bug fixes may not all the time be available.
{Hardware} Necessities and Preparation

Embarking on the Android OS journey together with your Raspberry Pi 3 requires a little bit little bit of planning and some important elements. Getting the proper {hardware} and setting it up accurately is the cornerstone of a easy and pleasing expertise. Consider it like baking a cake – you want the proper elements and the proper oven to get a scrumptious consequence.
Let’s get began on gathering our ‘elements’ and making ready the ‘oven’!
Important {Hardware} Elements
The success of working Android in your Raspberry Pi 3 hinges on having the proper gear. This is a rundown of what you will want:
- Raspberry Pi 3 Mannequin B or B+: That is the guts of the operation. The Mannequin B+ is usually most well-liked because of its barely improved efficiency and energy effectivity. Guarantee you could have the board itself.
- MicroSD Card: That is the place Android OS will reside. The velocity and capability of this card considerably influence efficiency. We’ll delve into the specifics shortly.
- Energy Provide: A dependable energy provide is essential. It ought to present no less than 2.5A at 5V. A poor energy provide can result in instability, crashes, and corrupted knowledge.
- MicroSD Card Reader: You will want a approach to join the microSD card to your pc for formatting and flashing the Android picture.
- HDMI Cable: To attach your Raspberry Pi to a monitor or TV for show.
- Monitor or TV: A show machine with an HDMI enter to view the Android interface.
- USB Keyboard and Mouse: These are important for navigating and interacting with the Android OS. You should use wired or wi-fi variations.
- Ethernet Cable (Elective): For a extra secure and doubtlessly quicker web connection than Wi-Fi.
- USB Hub (Elective): If you happen to plan on connecting a number of USB units, a powered USB hub may be helpful, particularly in case your energy provide is not strong.
MicroSD Card Specs
The microSD card is arguably probably the most important element, other than the Raspberry Pi itself. Its efficiency straight impacts the velocity and responsiveness of the Android OS. This is what you must know:
- Class: Goal for a Class 10 or, even higher, a UHS-I (Extremely Excessive Pace) card. These playing cards supply quicker learn and write speeds, leading to a snappier consumer expertise.
- Dimension: A minimal of 16GB is really helpful. Nevertheless, 32GB or 64GB gives more room for apps, knowledge, and future updates. Think about the scale of the functions and media you intend to make use of.
- Model: Respected manufacturers like SanDisk, Samsung, and Lexar are typically extra dependable and supply higher efficiency.
Making ready the MicroSD Card
Making ready the microSD card entails formatting it after which flashing the Android OS picture onto it. It is a essential step, so let’s break it down:
- Formatting the Card: Earlier than flashing the picture, you’ll want to format the microSD card. You should use a software just like the official SD Card Formatter (obtainable for Home windows and macOS) or a utility constructed into your working system. Select the FAT32 file system for compatibility.
- Downloading the Android Picture: Acquire the suitable Android OS picture in your Raspberry Pi 3 from a trusted supply. Guarantee it is suitable together with your particular Raspberry Pi mannequin.
- Flashing the Picture: Use a software program software like Etcher (really helpful for its simplicity and cross-platform compatibility) or Rufus (for Home windows) to flash the downloaded picture onto the formatted microSD card. Choose the picture file and the microSD card because the goal drive. This course of writes the Android OS to the cardboard.
- Ejecting the Card: As soon as the flashing course of is full, safely eject the microSD card out of your pc.
Essential Be aware: All the time again up any vital knowledge on the microSD card earlier than formatting it, as this course of will erase every part.
Potential {Hardware} Compatibility Points
Whereas the Raspberry Pi 3 is usually well-supported, some {hardware} compatibility points can come up. Consciousness of those potential issues will aid you troubleshoot for those who encounter difficulties.
- Wi-Fi: Whereas the Raspberry Pi 3 has built-in Wi-Fi, some Android distributions might have driver points. If you happen to expertise issues, think about using an Ethernet connection or a suitable USB Wi-Fi adapter.
- Bluetooth: Just like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth performance might not all the time be absolutely supported or might require further configuration.
- Touchscreen Shows: Touchscreen assist can range relying on the Android distribution and the particular show mannequin. Analysis compatibility earlier than buying a touchscreen.
- USB Gadgets: Some USB units, reminiscent of particular webcams or USB sound playing cards, may not be absolutely suitable or require further drivers. Check your units to make sure they operate accurately.
- Energy Provide: A weak energy provide is a typical offender for instability. Guarantee your energy provide meets the really helpful specs (2.5A at 5V).
Selecting an Android OS Picture
So, you’ve got determined to breathe new life into your Raspberry Pi 3 with the facility of Android! Wonderful alternative. Nevertheless, earlier than you begin flashing photos like a digital magician, you will want to choose the proper Android OS distribution. Consider it like selecting the proper paint coloration in your masterpiece – it units the tone for every part that follows. The panorama of Android on the Pi is numerous, providing choices tailor-made to numerous wants and talent ranges.
Let’s delve into the fascinating world of Android OS photos and discover the one which fits your undertaking finest.
Android OS Distributions for Raspberry Pi 3
The world of Android on the Raspberry Pi 3 is populated by a number of key gamers, every with its distinctive strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these variations is essential for making an knowledgeable resolution. The alternatives vary from general-purpose Android builds to specialised variations designed for particular duties. This is a have a look at some standard choices:
- LineageOS: A well-liked {custom} ROM primarily based on Android Open Supply Venture (AOSP). It affords a clear, streamlined expertise, usually with up to date options and safety patches in comparison with inventory Android. It’s a good selection for many who desire a acquainted Android expertise.
- Android Issues: (Although now deprecated and changed by Google’s new system) This was Google’s try at an OS particularly for Web of Issues (IoT) units. It was designed to be light-weight and targeted on embedded functions. Whereas improvement has stopped, you may discover some legacy builds nonetheless obtainable.
- AOSP (Android Open Supply Venture): The uncooked, unadulterated supply code of Android. Whereas technically not a pre-built “distribution,” it gives the inspiration upon which many different Android variations are constructed. Compiling AOSP for the Raspberry Pi 3 is a extra superior activity, requiring important technical experience.
- Different Customized Builds: Varied community-driven tasks and particular person builders have created their very own Android builds for the Raspberry Pi 3. These can supply distinctive options or optimizations however might range in stability and assist.
Options and Functionalities Comparability
Selecting the best Android OS in your Raspberry Pi 3 hinges on understanding the options and functionalities every distribution affords. Let’s break down the important thing facets with a useful desk:
| Title | Options | Compatibility | Execs/Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| LineageOS |
|
|
|
| Android Issues (Legacy) |
|
|
|
| AOSP (Android Open Supply Venture) |
|
|
|
| Different Customized Builds |
|
|
|
Downloading Android OS Photos
Able to make the leap? This is the place you could find the Android OS photos mentioned above:
- LineageOS: Go to the official LineageOS web site. Search for builds particularly in your Raspberry Pi 3 mannequin. Make sure you obtain the proper picture in your machine.
- Android Issues (Legacy): Chances are you’ll discover older photos on the Google builders web site or by way of group repositories. Nevertheless, because of its deprecation, assist is proscribed.
- AOSP: You will have to obtain the Android supply code from the AOSP repository and compile it your self. It is a complicated course of.
- Different Customized Builds: Search on-line boards, GitHub repositories, and group web sites devoted to Raspberry Pi tasks. All the time confirm the supply and status of the developer earlier than downloading and putting in any {custom} picture.
Flashing the Android OS Picture
Now that you have your picture and your {hardware} prepped, it is time to get the Android OS onto your microSD card. That is the place the rubber meets the street, the second of reality, the purpose the place your Raspberry Pi transforms from a set of digital elements right into a miniature Android powerhouse. The method entails transferring the Android OS picture file onto your microSD card, making it bootable and prepared for motion.
Let’s dive in and ensure this goes easily.The flashing course of is basically writing the Android OS picture onto the microSD card, making it bootable. This overwrites every part at the moment on the cardboard, so again up something vital beforehand! This step-by-step information will stroll you thru utilizing two standard and dependable instruments: Etcher and Raspberry Pi Imager. Each are free, straightforward to make use of, and obtainable for Home windows, macOS, and Linux.
Select the one you are most comfy with.
Utilizing Etcher to Flash the Android OS Picture
Etcher is a user-friendly, cross-platform software recognized for its simplicity and reliability. Its simple interface makes it an awesome alternative, particularly for learners.
- Obtain and Set up Etcher: First, head over to the official Etcher web site (balenaEtcher.com) and obtain the model in your working system. Comply with the set up directions, that are usually very simple.
- Insert Your microSD Card: Insert your microSD card into your pc’s card reader. Guarantee it is accurately acknowledged by your working system.
- Launch Etcher and Choose the Picture: Open Etcher. You will see a transparent interface with three most important buttons. Click on on “Flash from file” and browse to the Android OS picture file you downloaded earlier. Choose the `.img` or `.zip` file.
- Choose Your Goal Drive: Click on on “Choose goal.” Etcher will show an inventory of obtainable drives. Rigorously choose your microSD card. Double-check that you’ve got chosen the proper drive, as deciding on the fallacious one might result in knowledge loss.
- Flash the Picture: Click on on “Flash!” Etcher will start the method of writing the picture to the microSD card. You will see a progress bar indicating the progress, and Etcher will even confirm the write course of to make sure knowledge integrity.
- Verification and Completion: As soon as the flashing is full, Etcher will mechanically confirm the picture. This course of checks that the info written to the microSD card matches the unique picture. If verification fails, Etcher will provide you with a warning. If profitable, you will see a “Flash Full!” message.
- Eject and Use: After the flashing and verification are completed, Etcher will permit you to safely eject the microSD card. Now, you’ll be able to insert it into your Raspberry Pi 3 and boot up your Android OS.
Utilizing Raspberry Pi Imager to Flash the Android OS Picture
Raspberry Pi Imager is the official software developed by the Raspberry Pi Basis, making it a pure alternative for this undertaking. It simplifies the method, particularly for these new to this.
- Obtain and Set up Raspberry Pi Imager: You possibly can obtain Raspberry Pi Imager from the Raspberry Pi web site. It is also obtainable for Home windows, macOS, and Linux. Set up it utilizing the usual set up procedures in your working system.
- Insert Your microSD Card: As with Etcher, insert your microSD card into your pc’s card reader.
- Launch Raspberry Pi Imager and Choose the OS: Open Raspberry Pi Imager. Click on on “Select OS.” You will not discover Android OS straight listed right here. As a substitute, choose “Customized picture” to browse to your downloaded Android OS picture file (the `.img` or `.zip` file).
- Choose Your SD Card: Click on on “Select SD Card” and choose your microSD card from the record of obtainable drives. Once more, double-check that you’ve got chosen the proper drive.
- Write the Picture: Click on on “Write.” Raspberry Pi Imager will then write the picture to your microSD card. A progress bar will point out the progress. The software additionally verifies the written knowledge.
- Verification and Completion: Just like Etcher, Raspberry Pi Imager will confirm the written knowledge. If all goes effectively, you will obtain a affirmation message.
- Eject and Use: As soon as the method is full and verified, safely eject the microSD card out of your pc. You are now able to insert it into your Raspberry Pi 3.
Potential Points and Troubleshooting
Even with simple instruments, issues can typically go sideways. This is a breakdown of widespread points and the way to resolve them.
- Flashing Fails: If the flashing course of fails, there are some things to test.
- Corrupted Picture: Obtain the Android OS picture once more. Generally, a corrupted obtain is the offender. Confirm the checksum (if supplied) to make sure the file is undamaged.
- SD Card Points: The microSD card itself is likely to be defective. Strive a unique microSD card. Guarantee the cardboard is suitable together with your Raspberry Pi 3. Use a good model and keep away from playing cards with extraordinarily low scores.
- Write Safety: Some microSD playing cards have a bodily write-protection swap. Guarantee this swap is within the “write” place.
- Card Reader Issues: Your card reader is likely to be the issue. Strive a unique card reader or a unique USB port in your pc.
- Inadequate Permissions: On some working methods, chances are you’ll want administrator privileges to flash the picture. Run the flashing software as an administrator.
- Verification Errors: If the verification course of fails, it signifies that the info written to the cardboard does not match the unique picture. This often means the picture was corrupted throughout the write course of. Strive flashing the picture once more, utilizing a unique card, or a unique USB port.
- Card Not Acknowledged: If the flashing software does not acknowledge your microSD card, it is likely to be a difficulty with the cardboard reader, the cardboard itself, or the drivers in your pc. Strive a unique card reader, a unique USB port, or test for up to date drivers in your card reader.
- Raspberry Pi Will not Boot: In case your Raspberry Pi does not boot after flashing, there may very well be a number of causes:
- Incorrect Picture: Double-check that you’ve got downloaded the proper Android OS picture for the Raspberry Pi 3.
- Improper Formatting: The picture might not have been flashed accurately. Strive reflashing the picture.
- SD Card Compatibility: Whereas much less widespread, some microSD playing cards will not be absolutely suitable with the Raspberry Pi 3. Strive a unique card.
- Energy Provide: Make sure you’re utilizing a dependable energy provide that gives sufficient present (no less than 2.5A) to your Raspberry Pi 3. Inadequate energy is a typical reason for boot failures.
Booting and Preliminary Setup: Android Os On Raspberry Pi 3
Alright, you’ve got prepped your Raspberry Pi 3, chosen your Android OS picture, and flashed it onto your microSD card. Now, the second of reality has arrived: it is time to deliver your mini-Android to life! This part will stroll you thru the method, from powering up your Pi to navigating the preliminary setup screens. Think about this your Android Pi’s first breath, its digital awakening.
Booting the Raspberry Pi 3
After efficiently flashing the Android OS picture, the following step is as well your Raspberry Pi 3. This course of entails a couple of easy steps, but it surely’s essential to get them proper.As well your Raspberry Pi 3 with the newly flashed Android OS:
- Insert the microSD card: Rigorously insert the microSD card, containing the Android OS picture, into the microSD card slot in your Raspberry Pi 3. Guarantee it is correctly seated. Consider this because the mind transplant, the place the reminiscence card is the brand new mind.
- Join peripherals: Join the mandatory peripherals. This usually features a monitor (by way of HDMI), a keyboard, and a mouse (by way of USB). These are your eyes, ears, and palms, permitting you to work together with the system.
- Energy up: Join the facility provide to your Raspberry Pi 3. Guarantee the facility provide gives enough amperage (often 2.5A) to keep away from efficiency points. Watch because the magic occurs!
- Observe the boot sequence: Because the Raspberry Pi 3 boots, you will see a sequence of textual content and logos in your monitor. That is the boot sequence, a sequence of processes that masses the Android OS.
- Wait patiently: The preliminary boot might take a couple of minutes, particularly the primary time. Resist the urge to interrupt the method. Let the system do its factor.
Keep in mind, a secure energy provide is your finest good friend throughout this course of. A flaky energy provide can result in boot failures or, worse, knowledge corruption.
Preliminary Setup Course of
As soon as the Android OS has booted efficiently, you will be greeted with the preliminary setup screens. That is the place you configure the fundamentals of your Android expertise. That is like getting your new Android machine able to go.This is a breakdown of the everyday preliminary setup steps:
- Language Choice: The primary display often prompts you to pick your most well-liked language. Select your language from the supplied record. This units the language for the complete consumer interface.
- Wi-Fi Configuration: Subsequent, you will seemingly be requested to hook up with a Wi-Fi community. Choose your community from the obtainable record and enter the password if required. This connects your machine to the web.
- Date and Time Settings: The system will mechanically attempt to set the date and time. You may want to regulate the time zone or date/time settings manually. Correct time is vital for a lot of apps and providers.
- Google Account Setup: You will be prompted to sign up together with your Google account. You possibly can both sign up with an current account or create a brand new one. This unlocks entry to the Google Play Retailer and different Google providers.
- Phrases and Circumstances: You will be offered with the phrases and circumstances. Learn them (or no less than scroll by way of them!) and settle for them for those who agree. This ensures you are conscious of the authorized facets of utilizing the software program.
- Customization and Preferences: The setup might supply choices to customise your Android expertise, reminiscent of selecting a launcher, establishing safety features, and configuring notification preferences.
After finishing these steps, you must arrive on the Android house display, prepared to begin utilizing your Raspberry Pi 3 as an Android machine.
Troubleshooting Boot-Associated Issues
Generally, issues do not go as deliberate. Booting points can happen. Listed here are some widespread issues and their options:
- Black Display screen/No Show:
- Downside: You see nothing in your monitor.
- Options:
- Double-check the HDMI connection. Ensure that it is securely plugged into each the Raspberry Pi 3 and the monitor.
- Strive a unique HDMI cable. A defective cable can forestall a show sign.
- Make sure the monitor is ready to the proper HDMI enter.
- Confirm the facility provide is satisfactory. An underpowered Pi may not boot accurately.
- Boot Loop:
- Downside: The Raspberry Pi 3 repeatedly restarts with out absolutely booting.
- Options:
- Examine the microSD card. The picture could also be corrupted. Strive reflashing the Android OS picture onto the microSD card.
- Make sure the microSD card is suitable. Some playing cards might not work effectively with the Raspberry Pi 3.
- If you happen to’ve made any modifications to the boot configuration, attempt reverting them to the default settings.
- Caught at a Particular Display screen:
- Downside: The boot course of will get caught at a selected emblem or display.
- Options:
- Wait patiently. Generally, the preliminary boot can take some time.
- If it stays caught for an prolonged interval, attempt reflashing the Android OS picture.
- If the issue persists, the Android OS picture is likely to be incompatible together with your Raspberry Pi 3 mannequin. Strive a unique picture.
- Wi-Fi Points:
- Downside: You can not hook up with Wi-Fi.
- Options:
- Double-check the Wi-Fi password.
- Guarantee your Wi-Fi router is broadcasting on the two.4 GHz band (the Raspberry Pi 3’s built-in Wi-Fi usually solely helps 2.4 GHz).
- Transfer the Raspberry Pi 3 nearer to the Wi-Fi router.
- Strive a wired Ethernet connection to troubleshoot the Wi-Fi difficulty.
If you happen to encounter persistent issues, seek the advice of on-line boards or communities devoted to Raspberry Pi or Android OS on Raspberry Pi 3. The collective data of those communities is a beneficial useful resource.
Customization and Configuration
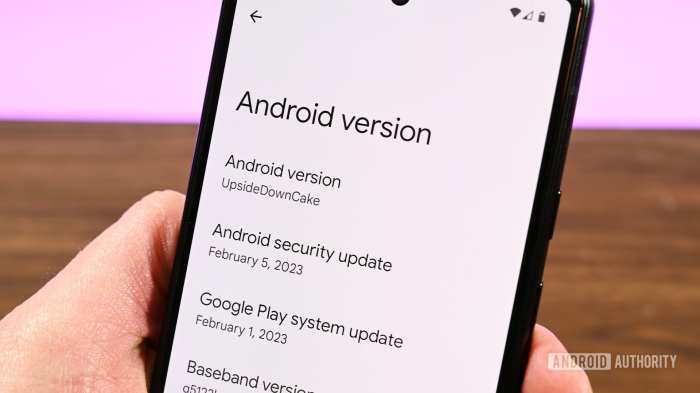
Now that you have Android up and working in your Raspberry Pi 3, let’s discuss making it really
yours*. This is not nearly performance; it is about persona. It is about turning a bare-bones OS right into a modern, personalised expertise. Consider it like giving your Pi a digital makeover, an opportunity to precise itself (and your preferences) by way of its interface. Let’s dive into the enjoyable stuff
making your Android on Pi expertise as distinctive as you’re.
Customizing the Android OS Interface
The Android interface is designed for flexibility, permitting for a excessive diploma of personalization. This customization extends past mere aesthetic modifications; it permits you to mildew the consumer expertise to suit your particular wants and preferences. From the launcher you utilize to the general theme and icon kinds, you could have the facility to create an setting that feels uniquely yours.
- Launcher Customization: The launcher is your private home display, the central hub of your Android expertise. You possibly can change it totally. There are lots of launchers obtainable by way of the Google Play Retailer (for those who’ve set it up, which we’ll get to), or you’ll be able to sideload APKs. Some standard choices embody:
- Nova Launcher: Extremely customizable, providing a big selection of choices for icon packs, grid sizes, gestures, and extra.
- Motion Launcher: Incorporates a distinctive “Quickpage” and “Covers” system for accessing apps and widgets shortly.
- Lawnchair Launcher: An open-source launcher that goals to offer a Pixel-like expertise.
Altering your launcher is often so simple as putting in it from the Play Retailer or by sideloading an APK, after which setting it as your default within the Android settings.
- Theme Modifications: Android permits for system-wide theme modifications. This alters the visible look of your interface, together with colours, fonts, and the general feel and appear.
- Utilizing Themes: Many launchers assist themes, permitting you to alter the complete look with a single click on.
- Customized Themes: You possibly can create your personal themes or obtain {custom} themes from the Play Retailer or different sources. This usually entails putting in theme engines like Substratum (if supported by your Android model).
- Icon Packs: Icon packs permit you to change the looks of your app icons. There are literally thousands of icon packs obtainable, starting from minimalist designs to vibrant, colourful units.
- Discovering Icon Packs: Search the Play Retailer for “icon packs.”
- Making use of Icon Packs: Most launchers have an possibility to use icon packs inside their settings.
- Widget Customization: Widgets are mini-applications that present info at a look. You possibly can add, take away, and resize widgets to customise your private home display. Android additionally affords a number of pre-installed widgets for varied capabilities, reminiscent of clocks, climate updates, and calendars.
Configuring Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Connectivity
Connectivity is vital. You will need your Raspberry Pi working Android to hook up with the web and different units. Organising Wi-Fi and Bluetooth is often simple.
- Wi-Fi Configuration:
- Accessing Wi-Fi Settings: Navigate to the “Settings” app, after which to “Community & web.”
- Deciding on Your Community: It’s best to see an inventory of obtainable Wi-Fi networks. Faucet in your community.
- Getting into Your Password: Enter your Wi-Fi password when prompted.
- Connecting: Android will try to hook up with the community. It’s best to see a Wi-Fi icon within the standing bar indicating a profitable connection.
- Bluetooth Configuration:
- Accessing Bluetooth Settings: In “Settings,” go to “Related units” after which “Bluetooth.”
- Turning on Bluetooth: Toggle the Bluetooth swap to “on.”
- Pairing Gadgets: Android will seek for obtainable Bluetooth units. Faucet on the machine you need to pair. Chances are you’ll have to enter a pairing code or settle for a connection request.
- Related Gadgets: As soon as paired, the machine will seem within the record of related units.
Putting in and Managing Functions
Getting apps in your Android on Raspberry Pi is important for increasing its performance. You may have a few major strategies for doing this: utilizing the Google Play Retailer (if accessible) and sideloading APK information.
- APK Set up: APK information are the set up packages for Android apps.
- Enabling Set up from Unknown Sources: Go to “Settings,” then “Apps,” and discover the choice to permit set up from unknown sources (usually beneath “Particular app entry”). This setting might range relying on the Android model. Allow this to put in apps from sources aside from the Play Retailer.
- Downloading APKs: Obtain the APK file for the app you need to set up. You’ll find APK information on web sites like APKMirror or APKPure.
- Putting in the APK: Use a file supervisor app to find the downloaded APK file and faucet on it. Comply with the on-screen prompts to put in the app.
- Google Play Retailer Entry: The Play Retailer gives a handy approach to uncover and set up apps.
- Organising a Google Account: You will want a Google account to entry the Play Retailer. Sign up to your current Google account or create a brand new one.
- Opening the Play Retailer: Find and open the Play Retailer app on your private home display or app drawer.
- Searching and Putting in Apps: Browse the Play Retailer to search out apps. Faucet on an app to view its particulars, after which faucet “Set up” to obtain and set up it.
- Managing Functions:
- Uninstalling Apps: Go to “Settings,” then “Apps,” and choose the app you need to uninstall. Faucet “Uninstall.”
- Updating Apps: The Play Retailer will notify you when updates can be found in your put in apps. You possibly can replace apps individually or replace all apps without delay.
- Managing App Permissions: Overview and handle app permissions in “Settings,” then “Apps.” This lets you management what knowledge and options every app can entry.
Optimizing Efficiency
Regardless that the Raspberry Pi 3 is a succesful machine, Android may be resource-intensive. You may encounter slowdowns or lag. This is the way to optimize efficiency.
- Disable Animations: Animations could make the interface really feel smoother, however in addition they eat sources. You possibly can disable or cut back animations within the “Developer choices” settings.
- Enabling Developer Choices: Go to “Settings,” then “About cellphone.” Faucet on the “Construct quantity” repeatedly (often seven occasions) till you see a message that claims you are actually a developer.
- Accessing Developer Choices: Return to the primary “Settings” menu. It’s best to now see a “Developer choices” entry.
- Disabling Animations: In “Developer choices,” search for settings associated to animation scale (window animation scale, transition animation scale, animator length scale). Set these to “Animation off” or cut back the dimensions to 0.5x.
- Restrict Background Processes: Android permits apps to run within the background, which may eat sources. You possibly can restrict the variety of background processes.
- Accessing the Restrict Background Processes Setting: This setting can also be present in “Developer choices.”
- Setting the Restrict: Select a restrict that fits your wants. You possibly can select from “Commonplace restrict,” “No background processes,” or a selected variety of processes. Bear in mind that limiting background processes too aggressively may forestall some apps from functioning accurately.
- Use Light-weight Apps: Some apps are designed to be much less resource-intensive. Think about using light-weight variations of standard apps. For instance, Fb Lite or Twitter Lite.
- Clear Cache and Knowledge: Repeatedly clear the cache and knowledge for apps that you just use incessantly. This may liberate cupboard space and enhance efficiency.
- Clearing Cache and Knowledge: Go to “Settings,” then “Apps,” choose the app, and faucet on “Storage.” You will discover choices to clear the cache and knowledge. Bear in mind that clearing knowledge will take away the app’s settings and saved knowledge.
- Overclocking (Use with Warning): Overclocking entails working the Raspberry Pi’s processor at the next velocity than its default setting. This may enhance efficiency, however it may additionally generate extra warmth and doubtlessly harm the machine if not completed rigorously. The effectiveness of overclocking varies primarily based on the Android construct and the particular Raspberry Pi 3 mannequin.
- Monitor System Sources: Use a system monitor app to trace CPU utilization, RAM utilization, and cupboard space. This may also help you determine apps which are consuming extreme sources.
Functions and Compatibility
The attract of Android on a Raspberry Pi 3 is plain, however a key consideration is the ecosystem of functions. The power to run your favourite apps, from productiveness instruments to video games, is what really transforms the Pi into a flexible machine. Nevertheless, the structure variations between a typical Android machine (ARM) and the Raspberry Pi 3 (ARMv7) can introduce complexities.
Understanding software compatibility is essential to maximizing the usefulness of your Android-powered Pi.
Android Software Compatibility on Raspberry Pi 3
Android functions are designed to run on a wide range of {hardware} configurations, however not all apps are created equal on the subject of the Raspberry Pi 3. The machine’s {hardware}, whereas succesful, is not as highly effective as the most recent smartphones or tablets. Furthermore, the ARMv7 structure of the Pi can typically result in compatibility points. This implies some apps might not operate accurately, or in any respect.That will help you navigate this, let’s delve into the specifics.
Functions Identified to Work Nicely
Plenty of functions have been efficiently examined and confirmed to operate adequately on the Raspberry Pi 3. The next record showcases a few of these suitable apps, categorized for readability.It is vital to do not forget that efficiency can range relying on the particular Android OS picture you’ve got chosen, the app itself, and the general load in your Raspberry Pi 3.
- Productiveness and Utility
- App Title: WPS Workplace
- Performance: An entire workplace suite, together with phrase processing, spreadsheets, and shows.
- Efficiency: Usually performs effectively, providing a usable expertise for doc creation and enhancing. Count on some lag with complicated paperwork.
- Internet Browsers
- App Title: Firefox (Android model)
- Performance: A well-liked internet browser providing a well-known searching expertise.
- Efficiency: Searching is usually easy, although complicated web sites with heavy JavaScript utilization might expertise slowdowns.
- Media Gamers
- App Title: VLC for Android
- Performance: A flexible media participant supporting a variety of audio and video codecs.
- Efficiency: Handles most video codecs with out points. Efficiency depends on the decision and codec of the video being performed.
- File Managers
- App Title: Strong Explorer
- Performance: A sturdy file supervisor offering entry to native storage, community shares, and cloud providers.
- Efficiency: Works easily, permitting for environment friendly file administration.
- Communication
- App Title: Telegram
- Performance: A messaging app with end-to-end encryption.
- Efficiency: Performs effectively, offering a seamless messaging expertise.
Addressing App Compatibility Points
Regardless of the successes, you will inevitably encounter apps that do not play good with the Raspberry Pi 3. The excellent news is that there are methods you’ll be able to make use of to mitigate these points.Think about these potential points and options:
- Software Optimization: Some functions will not be optimized for the particular {hardware} of the Raspberry Pi 3. This will result in efficiency points, crashes, or a failure to launch.
- Resolution: Search for different apps that provide comparable performance. If attainable, search out apps particularly designed or optimized for ARMv7 processors.
- {Hardware} Limitations: The Raspberry Pi 3 has restricted processing energy and reminiscence in comparison with trendy Android units.
- Resolution: Keep away from working a number of resource-intensive functions concurrently. Shut background apps to liberate system sources. Think about overclocking your Raspberry Pi 3 (with applicable cooling) to spice up efficiency.
- Compatibility with the Android OS picture: The Android OS picture you’ve got chosen might are compatible points with sure apps.
- Resolution: Experiment with totally different Android OS photos. Some photos are higher optimized for sure functions than others. Analysis the group to search out photos recognized for higher app compatibility.
- Lack of Google Play Providers: Some Android OS photos for the Raspberry Pi 3 might not embody Google Play Providers.
- Resolution: Apps that depend on Google Play Providers (e.g., for location providers, push notifications) might not work accurately. If Google Play Providers is obtainable, guarantee it is updated. Alternatively, think about sideloading different variations of the apps that do not depend on these providers.
Essential notice: Sideloading apps (putting in them from sources aside from the Google Play Retailer) can pose safety dangers. All the time obtain apps from trusted sources.
Efficiency Optimization
Let’s face it, working Android on a Raspberry Pi 3 is not precisely a velocity demon. The little board is a marvel of engineering, but it surely’s not packing the identical punch as a high-end smartphone. Nevertheless, with a little bit tweaking and a few intelligent changes, we will positively coax extra efficiency out of our tiny Android setup. Consider it as tuning a traditional automotive – you will not make it a Formulation 1 racer, however you’ll be able to actually make it purr like a well-oiled machine.
Strategies for Bettering Android OS Efficiency
Optimizing the efficiency of Android in your Raspberry Pi 3 entails a multi-faceted method. It is about maximizing the obtainable sources and minimizing pointless overhead. This implies tackling every part from the working system’s configuration to the {hardware}’s capabilities.
- Selecting the Proper Android OS Picture: Not all Android builds are created equal. Some are extra optimized for low-powered units just like the Raspberry Pi. Analysis and choose a picture particularly designed for the Pi 3, ideally one which’s light-weight and debloated (that means it has fewer pre-installed apps). Search for variations primarily based on Android Go or these with {custom} kernels tailor-made for the Pi’s {hardware}.
- Reduce Background Processes: Android is infamous for working quite a few background processes. These can eat treasured CPU cycles and RAM. Use the “Developer choices” (chances are you’ll have to allow them within the “About cellphone” part) to restrict background course of limits. Think about limiting them to “no background processes” to begin, after which enhance the restrict as wanted, relying in your app utilization.
- App Optimization: Be aware of the apps you put in. Keep away from resource-intensive apps, and go for “lite” variations every time attainable. Repeatedly clear app caches and knowledge to liberate cupboard space and enhance efficiency. Think about using a system app supervisor to disable or uninstall pointless pre-installed apps (however watch out to not take away something important for the OS to operate).
- Use a Light-weight Launcher: The default launcher generally is a useful resource hog. Change to a light-weight launcher, reminiscent of Nova Launcher (with minimal customization) or a launcher particularly designed for low-powered units.
- SD Card Pace: The velocity of your SD card considerably impacts efficiency, because it’s usually used as the first storage. Use a high-speed, Class 10 or UHS-I SD card. Sooner learn/write speeds will translate to faster app loading and general system responsiveness.
- Overclocking (with warning): Overclocking the Raspberry Pi 3 can present a noticeable efficiency increase, but it surely additionally will increase the chance of instability and {hardware} harm if not completed accurately. This will probably be lined in additional element in a later part.
- Correct Cooling: Overclocking and heavy use can generate warmth. Guarantee your Raspberry Pi 3 has satisfactory cooling. A heatsink is a naked minimal; a fan is really helpful, particularly for those who plan on overclocking.
- Community Optimization: A sluggish community connection could make the complete system really feel sluggish. Connect with your community by way of Ethernet every time attainable, because it’s typically quicker and extra secure than Wi-Fi. If utilizing Wi-Fi, guarantee a powerful sign.
Methods for Optimizing System Sources
Fantastic-tuning the system’s useful resource allocation is essential for squeezing each ounce of efficiency out of your Android setup. This entails making clever decisions about what runs, the way it runs, and the way a lot of the system’s sources it consumes.
- Disable Pointless Providers: Android runs quite a few providers within the background, a few of which can be pointless in your particular use case. Entry the “Settings” menu, then discover choices like “Accounts,” “Location,” and “Sync.” Disable options you do not want, reminiscent of location providers for those who do not require them. This frees up CPU cycles and RAM.
- Modify Show Settings: Excessive-resolution shows can put a pressure on the GPU. Decrease the display decision within the show settings if attainable. Think about disabling animations and transitions within the “Developer choices” to enhance responsiveness.
- Restrict Animations and Transitions: Animations and transitions, whereas visually interesting, eat processing energy. Within the “Developer choices,” you’ll be able to regulate or disable animation scales for home windows, transitions, and animator length. Setting these to 0.5x or disabling them altogether can considerably enhance responsiveness, particularly on slower {hardware}.
- Handle Storage Area: Regulate your cupboard space. A full storage drive can severely influence efficiency. Repeatedly filter pointless information, uninstall unused apps, and transfer massive information to an exterior storage machine.
- Disable or Reduce Widgets: Widgets are handy, however they continually replace within the background, consuming sources. Take away any widgets you do not actively use or restrict their replace frequency.
- Monitor Useful resource Utilization: Use a system monitor app to trace CPU utilization, RAM utilization, and storage utilization. It will aid you determine which apps or processes are consuming probably the most sources and determine potential bottlenecks. Many system monitoring apps can be found on the Google Play Retailer.
- Adoptable Storage (if supported): Some Android builds permit you to format an SD card as inside storage. This may enhance obtainable cupboard space for apps and knowledge, doubtlessly enhancing efficiency. Nevertheless, the efficiency of adoptable storage is dependent upon the velocity of the SD card.
Overclocking the Raspberry Pi 3 for Enhanced Efficiency
Overclocking entails working the Raspberry Pi 3’s processor at a clock velocity larger than its default setting. This may result in a noticeable efficiency increase, but it surely additionally comes with dangers. It is like giving your automotive a turbocharger – you get extra energy, however you additionally must be aware of the engine’s limits.
Essential Security Warnings:
- Overclocking can void your guarantee.
- Overclocking will increase the chance of {hardware} harm. Extreme warmth can result in CPU failure.
- Overclocking might trigger system instability. Your system might crash or freeze.
- All the time use satisfactory cooling. A heatsink is obligatory; a fan is very really helpful.
- Monitor the temperature. Maintain the CPU temperature under 80°C (ideally under 70°C).
How you can Overclock (Proceed with Warning):
Overclocking is often completed by enhancing the config.txt file on the SD card’s boot partition. This file comprises varied settings that management the Raspberry Pi’s {hardware} conduct. This is a primary information:
- Entry the config.txt file: Insert the SD card into your pc. The boot partition needs to be accessible. Open the
config.txtfile in a textual content editor. - Add or modify the overclocking settings: Add or modify the next traces within the
config.txtfile. Keep in mind to save lots of the file after making modifications.
over_voltage=2(This will increase the voltage to offer extra energy to the CPU. Begin with a low worth and enhance it cautiously.)
arm_freq=1300(This units the CPU clock velocity in MHz. The default is 1200 MHz. Experiment with totally different values. 1300 MHz is a typical and sometimes secure overclock.)
gpu_freq=500(This units the GPU clock velocity in MHz. Growing this could enhance graphics efficiency. Experiment with totally different values. 500 MHz is a typical overclock.)
- Reboot the Raspberry Pi: Safely eject the SD card and insert it again into the Raspberry Pi. Energy on the Pi and permit it as well.
- Monitor the temperature and stability: After booting, monitor the CPU temperature utilizing a system monitoring app. Check the system by working demanding apps or video games. If the system crashes or turns into unstable, cut back the overclocking settings (e.g., decrease the arm_freq or gpu_freq, or cut back over_voltage). If the temperature will get too excessive, cut back the overclocking settings or enhance cooling.
Instance Situation:
As an instance you are enjoying a graphically intensive recreation in your Android setup. With out overclocking, the sport stutters and lags. After overclocking the CPU to 1300 MHz and the GPU to 500 MHz (with applicable cooling and voltage changes), you discover a major enchancment in body charges and general responsiveness. The sport is now playable, and the expertise is far smoother.
Nevertheless, you additionally observe that the CPU temperature is larger, so you put in a small fan to make sure it stays inside protected working limits. This illustrates the sensible influence of overclocking, but in addition the significance of managing the related dangers.
Essential Concerns:
- Begin small and enhance regularly: Do not leap to excessive overclocking settings instantly. Improve the clock speeds and voltage in small increments and check for stability after every change.
- Check completely: Run demanding functions or video games to check the system’s stability beneath load.
- Monitor the temperature: Maintain a detailed eye on the CPU temperature utilizing a system monitoring app. If the temperature exceeds protected limits, cut back the overclocking settings or enhance cooling.
- Doc your modifications: Maintain a file of the overclocking settings you’ve got tried and their outcomes. It will aid you troubleshoot any points and revert to a secure configuration if essential.
Frequent Issues and Options

Operating Android on a Raspberry Pi 3 generally is a rewarding expertise, reworking your tiny pc into a flexible machine. Nevertheless, the trail to Android bliss is not all the time easy. You may encounter a couple of bumps alongside the way in which. This part equips you with the data to deal with widespread points, turning potential frustrations into alternatives for studying and enchancment. We’ll discover the everyday pitfalls and, extra importantly, the way to overcome them.
Wi-Fi Connectivity Issues
Wi-fi connectivity is essential for having fun with the total Android expertise. Sadly, Wi-Fi can typically be a supply of complications on a Raspberry Pi 3. Let’s delve into some widespread points and their fixes.
Listed here are some frequent Wi-Fi woes and the way to handle them:
- Weak Sign Power: The Raspberry Pi 3’s built-in Wi-Fi antenna generally is a bit delicate. Distance out of your router, obstacles like partitions, and interference from different units can weaken the sign.
- Resolution: Strive transferring your Raspberry Pi nearer to the router. Think about using a USB Wi-Fi adapter with a stronger antenna. A USB extension cable may also help place the adapter for optimum sign reception.
- Incorrect Wi-Fi Password: It is a traditional, however simply ignored. Double-check your Wi-Fi password.
- Resolution: Rigorously re-enter your Wi-Fi password within the Android settings. Make sure the caps lock key is not by accident enabled.
- Driver Points: Generally, the Android picture may not have the proper drivers in your Raspberry Pi 3’s Wi-Fi chip.
- Resolution: Examine the Android OS picture documentation or on-line boards for compatibility info. If essential, attempt a unique Android picture recognized to work effectively with the Raspberry Pi 3’s Wi-Fi.
- IP Deal with Conflicts: If one other machine in your community is utilizing the identical IP handle as your Raspberry Pi, you will have connectivity issues.
- Resolution: Configure your router to assign a static IP handle to your Raspberry Pi 3. Alternatively, you’ll be able to attempt utilizing DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), which mechanically assigns IP addresses, and reboot your Raspberry Pi.
- Router Compatibility: Older or much less widespread router configurations may not be absolutely suitable with the Android OS in your Raspberry Pi.
- Resolution: Guarantee your router’s firmware is updated. Examine the router’s settings to make sure it is not blocking visitors out of your Raspberry Pi. Seek the advice of on-line boards for particular router fashions and compatibility points.
Show Points
Getting the show to work accurately is prime. Show issues can vary from a clean display to incorrect resolutions.
Troubleshooting display-related points requires a scientific method. This is a breakdown:
- Clean Display screen or No Sign: That is usually the primary signal of bother.
- Resolution: Guarantee your HDMI cable is securely related to each your Raspberry Pi 3 and your monitor or TV. Strive a unique HDMI cable and a unique HDMI port in your show. Confirm the show is ready to the proper enter supply.
- Incorrect Decision: The show is likely to be displaying an incorrect decision, resulting in a distorted picture or black borders.
- Resolution: Navigate to the show settings throughout the Android OS. Modify the decision settings to match your monitor’s native decision. Experiment with totally different resolutions till you discover one which works finest. Some Android photos present a configuration file (usually referred to as “config.txt”) that may be edited to power a selected decision throughout boot.
- Display screen Flickering: Flickering may be brought on by varied elements, together with energy provide points or show driver issues.
- Resolution: Guarantee your Raspberry Pi 3 is receiving enough energy. Use a high-quality energy adapter that gives no less than 2.5 amps. Strive a unique HDMI cable. If the issue persists, the difficulty is likely to be associated to the Android picture’s show drivers; attempt a unique picture.
- Touchscreen Points (if relevant): If you happen to’re utilizing a touchscreen show, it may not be acknowledged or calibrated accurately.
- Resolution: Seek the advice of the documentation in your particular touchscreen show. You may want to put in further drivers or calibrate the touchscreen throughout the Android settings. Some Android photos have built-in touchscreen assist; others might require guide configuration.
Software Crashes
App crashes generally is a supply of annoyance. They will disrupt your workflow or leisure.
Software crashes are a typical frustration. Right here’s the way to handle them:
- Incompatible Functions: Not all Android apps are optimized for the Raspberry Pi 3’s {hardware}.
- Resolution: Examine the app’s compatibility info. Search on-line boards to see if different customers have efficiently run the app on their Raspberry Pi 3. Think about using different apps which are recognized to work effectively.
- Inadequate Sources: The Raspberry Pi 3 has restricted RAM and processing energy. Useful resource-intensive apps might crash.
- Resolution: Shut pointless apps working within the background. Think about using a lighter model of the app if obtainable. Optimize the app’s settings to cut back useful resource utilization (e.g., decrease graphics settings).
- Software program Bugs: The Android picture itself or the app you are utilizing may need bugs.
- Resolution: Replace the Android OS picture to the most recent model. Replace the app from the Google Play Retailer or different sources. Examine on-line boards or the app’s developer web site for recognized points and potential options.
- Corrupted App Knowledge: Generally, an app’s knowledge information can turn out to be corrupted, resulting in crashes.
- Resolution: Clear the app’s cache and knowledge within the Android settings (Settings > Apps > [App Name] > Storage). Uninstall and reinstall the app.
Sources for Additional Help and Assist
You are not alone on this journey. Quite a few sources can be found that can assist you troubleshoot and improve your Android-on-Raspberry Pi 3 expertise.
Listed here are some beneficial sources to contemplate:
- On-line Boards: On-line boards are treasure troves of knowledge.
- Particulars: Web sites just like the Raspberry Pi boards, XDA Builders, and devoted Android-on-Raspberry Pi boards are wonderful locations to ask questions, share experiences, and discover options. Seek for particular points you are going through; likelihood is another person has encountered the identical downside.
- Official Documentation: Seek the advice of the official documentation for the Android OS picture you are utilizing.
- Particulars: The documentation usually contains troubleshooting suggestions, incessantly requested questions, and directions for particular configurations.
- YouTube Tutorials: Video tutorials can present visible steerage.
- Particulars: Search YouTube for tutorials on Android on Raspberry Pi 3. These tutorials usually stroll you thru the setup course of and supply options to widespread issues.
- Developer Communities: Interact with the builders.
- Particulars: If you happen to’re utilizing a {custom} Android picture, think about reaching out to the builders of that picture for assist. They might have particular options or insights into your downside.
Superior Utilization and Initiatives
Alright, let’s dive into the thrilling realm the place your Raspberry Pi 3 working Android transcends the fundamentals and turns into a powerhouse of performance. We’re speaking about taking your little board and remodeling it into one thing really particular – a sensible house hub, a slick media middle, or perhaps a retro gaming console. The probabilities are huge, restricted solely by your creativeness (and maybe the processing energy of the Pi 3, however hey, we’ll work with what we have got!).
Get able to unleash the total potential of your Android-powered Raspberry Pi!
Design Superior Initiatives or Use Instances
The fantastic thing about Android on a Raspberry Pi 3 lies in its versatility. Think about the next undertaking concepts:* Good Dwelling Management Middle: Think about controlling your lights, thermostat, safety system, and extra, all from a single Android interface displayed on a touchscreen related to your Pi. You may use apps like Dwelling Assistant or openHAB to handle your sensible house units.* Media Middle: Remodel your TV into a sensible leisure hub utilizing Kodi, Plex, or different media middle functions.
This lets you stream films, TV exhibits, and music from varied sources.* Retro Gaming Console: Emulate traditional recreation consoles just like the NES, SNES, and PlayStation utilizing emulators like RetroArch. Pair a Bluetooth controller and relive your childhood gaming reminiscences.* Digital Signage: Show info, commercials, or bulletins on a display in a public house. This may very well be helpful for companies, colleges, or group facilities.* Customized Android Pill: Construct a devoted Android pill with a touchscreen and {custom} enclosure for particular duties, reminiscent of a dashboard in your automotive or a management panel in your house automation system.* IoT Hub: Join sensors and different {hardware} elements to create an Web of Issues (IoT) hub.
Acquire knowledge from sensors, analyze it, and management units primarily based on the collected info.
Setting Up a Media Middle Utilizing Kodi on Android
Making a media middle with Kodi in your Android-powered Raspberry Pi 3 is a comparatively simple course of. This is the way to get began:* Set up Kodi: Discover the Kodi software within the Google Play Retailer (if obtainable in your Android OS picture) or obtain the APK file from the Kodi web site and set up it.* Configure Community Settings: Guarantee your Raspberry Pi is related to your private home community, both by way of Wi-Fi or Ethernet.
Be aware the IP handle assigned to your Pi.* Add Media Sources: In Kodi, navigate to the “Movies” or “Music” part and add your media sources. These may very well be native folders on a related USB drive, community shares (SMB, NFS), or on-line streaming providers.* Set up Add-ons: Improve your Kodi expertise by putting in add-ons for streaming providers, climate updates, and different options.
Browse the add-on repository inside Kodi or set up add-ons from exterior sources.* Customise the Interface: Personalize the looks of Kodi by altering the pores and skin, configuring the menu format, and adjusting different settings to your preferences.* Check Playback: Choose a video or music file and check the playback to make sure every part is working accurately.* Optimize for Efficiency: If you happen to encounter any efficiency points, think about lowering the video decision, disabling pointless add-ons, and optimizing the Kodi settings in your {hardware}.
Incorporating Sensors and Different {Hardware} Elements
The actual magic occurs if you begin connecting {hardware} to your Android-powered Raspberry Pi
3. Listed here are some concepts
* Join Sensors: Use the Raspberry Pi’s GPIO pins to attach sensors reminiscent of temperature sensors, humidity sensors, mild sensors, and movement detectors. You should use apps or custom-developed Android functions to learn knowledge from these sensors.* Management Relays and Actuators: Management exterior units like lights, motors, and home equipment by connecting relays to the GPIO pins. This allows you to construct a house automation system.* Interface with Cameras: Join a USB webcam or a Raspberry Pi digicam module to seize photos or video.
You should use Android apps to view and handle the digicam feed.* Use a Touchscreen: Join a touchscreen show to create a user-friendly interface in your tasks.* Make the most of Bluetooth and Wi-Fi: Reap the benefits of the Raspberry Pi 3’s built-in Bluetooth and Wi-Fi capabilities to hook up with different units, reminiscent of Bluetooth audio system, or entry the web.* Combine with Arduino or different microcontrollers: Use serial communication (UART) to attach your Raspberry Pi to an Arduino board.
The Arduino can deal with real-time duties, and the Raspberry Pi can present a consumer interface or knowledge evaluation.Keep in mind to contemplate energy necessities, compatibility points, and software program improvement when integrating {hardware} elements. For instance, when connecting a number of USB units, a powered USB hub is likely to be essential to make sure enough energy for all units.
Safety Concerns
Let’s discuss retaining your Android OS in your Raspberry Pi 3 protected and sound. It is not nearly getting the OS up and working; it is about ensuring your knowledge and your privateness are protected. Consider it like this: you would not go away your entrance door unlocked, proper? The identical goes in your digital world. Securing your Android set up is essential, particularly contemplating the potential vulnerabilities of a {custom} setup.
Securing the Android OS Set up
Consider your Raspberry Pi working Android as a miniature fortress. You’ve got constructed the partitions, now you’ll want to set up the safety methods. This entails a couple of key steps to fortify your setup.Enabling Display screen Lock is the primary line of protection.
- Go to Settings.
- Discover the Safety part.
- Select a display lock technique, reminiscent of a PIN, sample, or password. A robust password, with a mixture of letters, numbers, and symbols, is really helpful. This prevents unauthorized entry in case your Pi is left unattended.
Putting in Safety Functions is one other essential step.
- Think about putting in a good antivirus software from the Google Play Retailer (if accessible in your Android construct).
- These apps scan for malware and viruses, providing real-time safety.
- Maintain the antivirus software program up to date to make sure it is efficient towards the most recent threats.
Protecting the Android OS up to date is extraordinarily vital.
- Examine for system updates frequently.
- Updates usually embody safety patches that handle recognized vulnerabilities.
- Comply with the directions supplied by your chosen Android OS picture supplier for updating the system.
Understanding Permissions is important.
- Be aware of the permissions you grant to functions.
- Solely grant essential permissions. For example, an app requesting entry to your contacts may increase a purple flag if it is a easy recreation.
- Repeatedly overview the permissions granted to your put in apps.
Defending Consumer Knowledge and Privateness
Past the fundamentals, safeguarding your private knowledge and privateness is paramount. Your Raspberry Pi, like all machine related to the web, is a possible goal.Use a VPN (Digital Personal Community) to encrypt your web visitors.
- A VPN creates a safe tunnel in your knowledge, making it tougher for hackers to intercept your info.
- Select a dependable VPN supplier with a powerful status for privateness.
Be cautious in regards to the info you share on-line.
- Keep away from sharing delicate private info, reminiscent of your handle or monetary particulars, on untrusted web sites or apps.
- Be cautious of phishing makes an attempt, which attempt to trick you into revealing your login credentials or different delicate knowledge.
Overview app permissions and knowledge entry frequently.
- Repeatedly overview the permissions granted to your put in apps.
- Think about the varieties of knowledge every app accesses.
- Revoke permissions for those who’re uncomfortable with an app’s entry to your knowledge.
Use robust passwords and allow two-factor authentication.
- Use robust, distinctive passwords for all of your on-line accounts.
- Allow two-factor authentication (2FA) every time attainable. This provides an additional layer of safety by requiring a second verification technique, reminiscent of a code despatched to your cellphone.
Think about using privacy-focused browsers and engines like google.
- Privateness-focused browsers and engines like google prioritize consumer privateness and decrease knowledge monitoring.
- Examples embody DuckDuckGo for search and Firefox with privacy-enhancing extensions.
Repeatedly again up your knowledge.
- Again up your vital knowledge to a safe location, reminiscent of an exterior exhausting drive or a cloud storage service.
- This ensures you can recuperate your knowledge in case of a safety breach or knowledge loss.
Future Developments
The world of Android on Raspberry Pi is much from static. It is a vibrant ecosystem, continually evolving with new prospects on the horizon. From software program developments to {hardware} improvements, the longer term guarantees thrilling enhancements that may form how we work together with this highly effective mixture. The trajectory suggests an more and more seamless and feature-rich expertise, broadening the attraction and usefulness of Android on the Raspberry Pi.
{Hardware} Developments
The Raspberry Pi basis and the broader tech group are all the time striving to push the boundaries of what is attainable. New {hardware} iterations are anticipated to offer important boosts to efficiency and capabilities, which straight impacts the Android expertise.
- Enhanced Processing Energy: Future Raspberry Pi fashions are prone to incorporate extra highly effective processors. Think about a quad-core processor evolving into an octa-core behemoth, able to dealing with demanding Android functions with ease. This interprets to smoother multitasking, quicker software loading occasions, and a extra responsive general system. Consider enjoying graphically intensive video games or working a number of functions concurrently with none noticeable lag.
- Elevated RAM Capability: Extra RAM permits for extra functions to be energetic without delay, and bigger datasets to be processed. Present fashions, with their limitations, can typically wrestle with demanding duties. Future fashions will seemingly characteristic considerably elevated RAM, enabling customers to run extra complicated Android functions, deal with bigger information, and expertise a extra fluid consumer interface. That is notably helpful for customers who need to use their Raspberry Pi as a mini-server or for media consumption.
- Improved Graphics Processing: The combination of extra highly effective GPUs (Graphics Processing Items) is essential for Android on Raspberry Pi, particularly for gaming and multimedia functions. Count on future fashions to boast enhanced graphics capabilities, enabling smoother gameplay, larger resolutions, and assist for extra demanding visible results. It will remodel the Raspberry Pi right into a succesful platform for leisure and inventive tasks.
- Optimized Energy Administration: Environment friendly energy administration is essential for the Raspberry Pi’s portability and usefulness. Future developments will deal with optimizing energy consumption, resulting in longer battery life for moveable tasks and decreased warmth era. That is vital for a extra seamless consumer expertise, permitting for longer utilization occasions with out worrying about overheating or working out of energy.
Software program Improvements
Past the {hardware}, software program improvement performs a important position in shaping the way forward for Android on Raspberry Pi.
- Optimized Android Builds: Count on continued refinement of Android builds particularly tailor-made for Raspberry Pi. Builders are continually working to optimize the working system for the distinctive {hardware} constraints of those units. This implies improved efficiency, higher compatibility, and a extra streamlined consumer expertise. The objective is to create an Android expertise that feels as native and responsive as attainable on the Raspberry Pi.
- Improved Driver Assist: Enhanced driver assist is significant for making certain compatibility with a variety of peripherals, reminiscent of cameras, sensors, and shows. Count on higher assist for varied {hardware} elements, permitting customers to attach and make the most of a wider array of units with their Raspberry Pi working Android. This expands the chances for inventive tasks and sensible functions.
- Enhanced Software Compatibility: The Android ecosystem is huge, and making certain compatibility with a variety of functions is essential. Builders are working to deal with compatibility points and optimize functions for the Raspberry Pi platform. It will permit customers to get pleasure from their favourite Android apps with out encountering efficiency bottlenecks or compatibility glitches.
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: The power to obtain over-the-air updates is important for sustaining a safe and up-to-date system. Count on future Android builds to assist OTA updates, permitting customers to simply set up new variations of the working system with out the necessity for guide flashing. This simplifies the upkeep course of and ensures customers all the time have entry to the most recent options and safety patches.
Rising Applied sciences and Traits
The panorama of expertise is continually shifting, and several other rising developments are poised to influence the way forward for Android on Raspberry Pi.
- Synthetic Intelligence (AI) and Machine Studying (ML): The combination of AI and ML capabilities will open up thrilling new prospects for Android on Raspberry Pi. Think about utilizing your Raspberry Pi to construct sensible house units, analyze knowledge from sensors, and even create easy AI-powered functions. This might result in a wave of revolutionary tasks that leverage the facility of AI on a compact and inexpensive platform.
- Web of Issues (IoT): The Raspberry Pi is already a well-liked platform for IoT tasks, and Android’s integration with IoT units will proceed to evolve. Count on to see extra seamless integration with IoT platforms and units, permitting customers to regulate and monitor their sensible house units straight from their Android-powered Raspberry Pi. This might create a extra built-in and user-friendly IoT expertise.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing entails processing knowledge nearer to the supply, lowering latency and enhancing responsiveness. The Raspberry Pi is well-suited for edge computing functions, and Android’s assist for edge computing frameworks will seemingly enhance. This might allow the event of extra responsive and environment friendly functions for duties reminiscent of knowledge evaluation and real-time monitoring.
- Voice Management and Good Assistants: The combination of voice management and sensible assistants, reminiscent of Google Assistant, will turn out to be more and more prevalent. It will allow customers to work together with their Android-powered Raspberry Pi utilizing voice instructions, making it simpler to regulate units, entry info, and automate duties.
