Embark on a journey into the heart of your Android device, where the lens of your camera awaits your command. How to allow access to camera on android isn’t just a technical query; it’s an invitation to explore the digital world, where memories are captured, connections are forged, and creativity knows no bounds. Think of it as unlocking a secret portal, a gateway to a realm of instant communication, creative expression, and seamless interaction with the world around you.
From snapping quick photos to participating in video calls that bridge distances, your camera is an indispensable tool, but like any powerful instrument, it requires proper handling.
This guide will illuminate the path, revealing the secrets of camera permissions on Android. We’ll navigate the settings labyrinth, demystify the app permission process, and equip you with the knowledge to control your device’s camera access. Whether you’re a tech novice or a seasoned Android aficionado, prepare to become a master of your digital domain, ensuring your privacy while harnessing the full potential of your camera.
Get ready to discover the ease and simplicity of managing your camera permissions, unlocking a world of visual possibilities at your fingertips.
Understanding Camera Permissions on Android
Let’s delve into the fascinating world of camera permissions on Android, a crucial aspect of mobile device functionality and user privacy. It’s a topic that touches upon how we interact with our phones, the applications we use, and the data we generate. Understanding these permissions is the first step in safeguarding your digital life.
Fundamental Concepts of Camera Permissions
Android camera permissions are essentially gatekeepers, controlling which applications can access your device’s camera hardware. They’re a fundamental security feature designed to protect your privacy. When an app requests camera permission, it’s asking for the right to capture photos, record videos, and potentially even stream live video feeds. This access isn’t granted automatically; the user has the final say. The Android operating system presents a clear prompt, asking the user to either “Allow” or “Deny” the requested permission.
This granular control is a cornerstone of Android’s approach to user privacy.
Why Camera Access is Crucial for Various Applications
Camera access is the lifeblood of many applications, enabling a wide range of functionalities. Imagine a world without the ability to snap a quick photo or record a video – it’s almost unimaginable in today’s digital landscape. From capturing memories to facilitating communication and even powering augmented reality experiences, camera access is essential.
- Social Media: Platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and Snapchat rely heavily on camera access for users to create and share photos and videos. Without it, these apps would be fundamentally broken.
- Communication Apps: Video calls on apps like WhatsApp, Zoom, and Google Meet are impossible without camera permission. This feature has become indispensable for personal and professional communication.
- Barcode and QR Code Scanners: Applications designed to scan barcodes and QR codes need camera access to read the information encoded in these visual elements. Think of mobile payment apps or product information scanners.
- Document Scanning: Apps like Adobe Scan or CamScanner use the camera to capture images of documents, converting them into digital files. This is a common function for both personal and professional use.
- Augmented Reality (AR) Applications: AR apps, such as those used for virtual try-ons or interactive games, use the camera to overlay digital content onto the real world. This requires continuous access to the camera feed.
Potential Privacy Implications of Granting Camera Access
While camera access unlocks a wealth of features, it’s essential to be aware of the potential privacy implications. Granting permission to an app means trusting that app to handle your camera data responsibly. Misuse of camera access could lead to serious privacy breaches.
- Unauthorized Recording: A malicious app could potentially record video or take photos without your knowledge. This could happen in the background, without any visible indication.
- Data Collection: Apps could use camera data to collect information about your surroundings, your identity, or your activities. This data could then be used for targeted advertising or sold to third parties.
- Security Vulnerabilities: If an app has security vulnerabilities, it could be exploited by hackers to gain access to your camera feed. This could lead to surveillance or the theft of sensitive information.
- Loss of Control: Once permission is granted, it can be difficult to monitor how an app is using your camera. While Android provides tools to manage permissions, it’s important to be vigilant about which apps you grant access to.
Accessing Android Settings for Camera Permissions
So, you’ve grasped the fundamentals of camera permissions on Android. Now, let’s dive into how to actuallyget* to the settings where you can tweak those permissions. Think of it like a treasure hunt – the camera’s permission settings are the loot, and accessing Android settings is the map! It’s not always a straightforward path, as Android versions and device manufacturers sprinkle their own unique flavor on the journey.Navigating to the settings for camera permissions is a crucial step in ensuring your apps behave as expected and respect your privacy.
This involves knowing how to reach the app settings, a process that can differ slightly depending on your Android version and the specific device you’re using. We’ll break down the common methods and guide you through the process.
Identifying Methods for Accessing App Settings
There are several routes to reach the app settings, the control center for all things app-related, including camera permissions. These methods usually involve using the system settings app, which is a pre-installed app on every Android device.
- Method 1: The Settings App. This is the most direct approach. Look for an app icon that typically resembles a gear or cogwheel. It’s usually found on your home screen or in your app drawer. Once opened, you’ll need to navigate through the menus, often looking for “Apps,” “Applications,” or “App Manager.”
- Method 2: Through the App Icon. Long-pressing (holding your finger down) on an app icon, either on your home screen or in the app drawer, often brings up a contextual menu. One of the options here should be “App info” or something similar. Selecting this will directly take you to the app’s settings page.
- Method 3: Within the App Itself. Some apps provide a direct link to their settings within their own interface. This is less common for core system settings like camera permissions, but it’s worth checking the app’s settings menu just in case.
Navigating to the “Apps” or “App Manager” Section
Once you’ve opened the Settings app, the next step is to locate the “Apps” or “App Manager” section. This is where the magic happens; where you’ll find the list of all installed apps on your device. The naming and exact location of this section can vary depending on your Android version and the manufacturer of your phone (Samsung, Google Pixel, etc.).
- Finding “Apps” or “App Manager”: After opening the Settings app, scroll through the list of options. Common names for this section include “Apps,” “Applications,” “App Manager,” or “Installed apps.” If you can’t find it immediately, try using the search bar at the top of the Settings app and typing in “apps.”
- Understanding Variations:
- Android Stock (e.g., Google Pixel): Often, the “Apps” section is readily visible in the main Settings menu.
- Samsung: Samsung devices might have a section called “Apps” or “Application manager” within the “Apps” menu.
- Other Manufacturers: Manufacturers like OnePlus, Xiaomi, and others often have their own custom Android skins, so the exact wording and placement might differ. However, the core concept remains the same.
Locating the Specific App for Managing Camera Permissions
Once you’ve found the “Apps” or “App Manager” section, you’re ready to pinpoint the app whose camera permissions you want to manage. This is where you’ll be able to grant, deny, or customize the app’s access to your device’s camera.
- Finding the App: Within the “Apps” or “App Manager” section, you’ll see a list of all installed apps, usually arranged alphabetically. Scroll through the list and locate the app you’re interested in (e.g., “Instagram,” “WhatsApp,” or any other app that uses the camera).
- Accessing App Info: Tap on the app’s name to open its “App info” screen. This screen provides detailed information about the app, including storage usage, battery usage, and, crucially, its permissions.
- Permissions Section: Look for a section labeled “Permissions” or something similar on the “App info” screen. This is where you’ll find the list of permissions the app requests, including the camera permission.
Steps for Different Android Versions
The steps to access app settings and manage permissions can vary depending on the Android version. Below is a table illustrating the process for several common Android versions.
| Android Version | Steps | Screenshot | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Android 13 (and later) |
|
A screenshot showing the Settings app, with the “Apps” option highlighted. Another screenshot showing the “App info” screen for an app, with the “Permissions” option highlighted. Finally, a screenshot showing the Permissions screen with the “Camera” permission and a toggle switch to enable/disable. | Android 13 and later versions generally have a consistent interface for managing app permissions. The layout is user-friendly, and the steps are straightforward. |
| Android 12 |
|
A screenshot showing the Settings app, with the “Apps & notifications” option highlighted. Another screenshot showing the “App info” screen for an app, with the “Permissions” option highlighted. Finally, a screenshot showing the Permissions screen with the “Camera” permission and a toggle switch to enable/disable. | Android 12 introduced enhanced privacy features, making permission management more transparent and user-friendly. |
| Android 11 |
|
A screenshot showing the Settings app, with the “Apps & notifications” option highlighted. Another screenshot showing the “App info” screen for an app, with the “Permissions” option highlighted. Finally, a screenshot showing the Permissions screen with the “Camera” permission and a toggle switch to enable/disable. | Android 11 continued the trend of improving permission management, with clearer options and more control for the user. |
| Android 10 |
|
A screenshot showing the Settings app, with the “Apps & notifications” option highlighted. Another screenshot showing the “App info” screen for an app, with the “Permissions” option highlighted. Finally, a screenshot showing the Permissions screen with the “Camera” permission and a toggle switch to enable/disable. | Android 10 introduced more granular control over app permissions, giving users greater control over their privacy. |
| Android 9 (Pie) |
|
A screenshot showing the Settings app, with the “Apps & notifications” option highlighted. Another screenshot showing the “App info” screen for an app, with the “Permissions” option highlighted. Finally, a screenshot showing the Permissions screen with the “Camera” permission and a toggle switch to enable/disable. | Android 9 (Pie) introduced further refinements to the permission management system, offering a more streamlined experience. |
| Older Android Versions (e.g., Android 8 Oreo and earlier) |
|
A screenshot showing the Settings app, with the “Apps” or “Applications” option highlighted. Another screenshot showing the “App info” screen for an app, with the “Permissions” option highlighted. Finally, a screenshot showing the Permissions screen with the “Camera” permission and a toggle switch to enable/disable. | Older Android versions have a slightly different interface, but the core steps remain similar. The “Permissions” section might be located in a slightly different place within the app’s settings. |
Granting Camera Access
Now that you’ve got a handle on the why and where of camera permissions, let’s dive into the nitty-gritty: how to actuallygive* an app the green light to use your camera. This is the part where you, the benevolent gatekeeper of your phone’s inner workings, decide which apps get to peek through the lens.
Finding the “Permissions” Section
Navigating to the permissions settings is like a treasure hunt, but with a map. Here’s how to find the “Permissions” section within an app’s settings: You can find the permissions settings within an app’s settings. The precise location varies slightly depending on your Android version and the manufacturer of your device (Samsung, Google Pixel, etc.), but the general process remains the same.
- Method 1: Through the App Drawer. Locate the app icon on your home screen or in your app drawer. Long-press (or tap and hold) the app icon. A menu will appear, often with options like “App info” or an “i” icon. Tap this to open the app’s settings.
- Method 2: Through the Settings App. Open the main “Settings” app on your device. This is usually represented by a gear icon. Scroll down and look for a section labeled “Apps,” “Applications,” or something similar. Tap on it.
- Method 3: Finding the App. Inside the “Apps” section, you’ll see a list of all the apps installed on your device. Scroll through the list or use the search bar to find the app you’re interested in. Tap on the app’s name to open its settings.
- Method 4: Permissions Section. Once you’re in the app’s settings, look for a section labeled “Permissions.” It might also be called “App permissions” or “Permissions manager.” This is where the magic happens.
This section usually displays a list of all the permissions the app requests, including camera, microphone, storage, and location.
Enabling Camera Permissions
Granting camera access is a straightforward process, but let’s make sure it’s crystal clear:
- Step 1: Locate the Camera Permission. Within the “Permissions” section of the app’s settings, look for the “Camera” permission. It might be listed as “Camera,” “Take pictures and record video,” or something similar.
- Step 2: Tap on the Camera Permission. Tap on the “Camera” permission to open its settings. You’ll typically see a screen with options to “Allow” or “Deny” camera access.
- Step 3: Choose Your Option.
- Allow: If you want the app to have access to your camera, tap “Allow.” The app will now be able to use your camera when needed.
- Deny: If you don’t want the app to access your camera, tap “Deny.” The app will not be able to use your camera.
- Allow only while using the app: Some Android versions offer the option to grant permission only while the app is in use. This is a good middle ground for security.
- Step 4: Confirm Your Choice. After tapping “Allow” or “Deny,” the permission status will update. You might need to tap “Back” to return to the app’s settings.
If the camera permission is already enabled, but the app still can’t access the camera, there could be several reasons.
“Double-check that the permission is enabled in the app’s settings, and then troubleshoot any potential conflicts with other apps or system-level settings.”
First-Time Camera Access Requests
The first time an app asks for camera access is like a digital first date: a moment of anticipation. Here’s what happens:
- The Prompt. When an app attempts to use the camera for the first time, a system prompt will appear on your screen. This prompt will ask if you want to allow the app to access your camera.
- Options. The prompt will typically give you two options: “Allow” or “Deny.”
- The Choice. Your choice will determine the app’s future access to your camera. If you choose “Allow,” the app will be granted permission, and you won’t be prompted again unless you change your mind later. If you choose “Deny,” the app will not be able to access your camera, and you might be prompted again in the future if the app needs camera access for a specific feature.
- The “Don’t Ask Again” Option. Some prompts might also include a “Don’t ask again” or similar option. If you select this, your choice will be remembered, and you won’t be prompted again for that particular permission for that app. Be cautious when using this option, as it could inadvertently grant or deny access without your explicit consent in the future.
For example, imagine you are using a new social media app. You try to take a photo to post. The app, for the first time, requests access to your camera. You will be presented with the “Allow” or “Deny” option. Choosing “Allow” grants immediate access, while “Deny” restricts it, possibly hindering your ability to use the app’s photo-taking features.
Troubleshooting Camera Access Issues
Sometimes, even after granting permission, an app might still struggle to access your camera. Here’s what to do if the camera permission is enabled, but the app is still having trouble:
- Check the App’s Settings Again. Double-check that the camera permission is indeed enabled within the app’s settings, following the steps Artikeld above. Sometimes, a setting might have been accidentally disabled.
- Restart the App. Close the app completely and reopen it. This can often resolve temporary glitches or conflicts.
- Restart Your Device. A full device restart can clear up various system-level issues that might be interfering with camera access.
- Check for System-Level Restrictions. Some devices have system-level settings that can override app-specific permissions. Look for settings related to camera access in your device’s main “Settings” app. For example, some devices have a global switch to disable all camera access.
- Clear the App’s Cache and Data. In the app’s settings (in the “Apps” section), try clearing the app’s cache and data. This can sometimes resolve issues caused by corrupted files. Note that clearing the data will delete app-specific settings and data, so back up anything important first.
- Update the App. Make sure you have the latest version of the app installed from the Google Play Store. App updates often include bug fixes and performance improvements that can address camera access problems.
- Update Your Device’s Operating System. Ensure your Android operating system is up-to-date. System updates often include security patches and improvements that can affect app permissions and camera functionality.
- Check for Conflicts with Other Apps. Some apps, particularly those that use the camera or microphone, might conflict with each other. Try closing other apps that could be using the camera or microphone in the background.
- Contact the App Developer. If none of the above steps work, there might be a bug within the app itself. Contact the app developer for support. You can usually find contact information on the app’s Google Play Store page or within the app’s settings.
- Factory Reset (Last Resort). As a last resort, you can perform a factory reset of your device. This will erase all data and settings, so back up everything important beforehand. A factory reset can sometimes resolve deep-seated system issues that are preventing camera access.
Remember, troubleshooting camera access can be a process of elimination. Work through these steps methodically to identify and resolve the issue.
Troubleshooting Camera Access Issues: How To Allow Access To Camera On Android
Camera access problems can be frustrating, turning a simple task into a tech support odyssey. But don’t despair! Many issues are easily resolved with a little troubleshooting. This section equips you with the knowledge to diagnose and fix common camera access roadblocks on your Android device.
Common Reasons for Camera Access Failures
Understanding why your app might be denied access to the camera is the first step toward a solution. Several factors can contribute to this issue, ranging from simple permission oversights to more complex hardware or software conflicts.
- Permission Denials: The most frequent culprit. If an app hasn’t been granted camera permission, it simply cannot access the camera. This is a crucial security feature designed to protect your privacy.
- App Crashes or Bugs: Software glitches within the app itself can prevent camera initialization or use. A corrupted app installation or outdated version can be to blame.
- Hardware Issues: While less common, physical damage to the camera lens or internal components can render the camera unusable. A dropped phone, for instance, could damage the camera module.
- Camera in Use by Another App: Android only allows one app to use the camera at a time. If another app is actively using the camera (e.g., a video call or another camera app), the requested app will be blocked.
- Operating System Updates: Sometimes, updates to the Android operating system can introduce compatibility issues or change the way permissions are handled.
- Restricted Profiles or Parental Controls: On devices with multiple user profiles, a restricted profile might not have camera access enabled. Similarly, parental control settings can limit camera usage.
Checking for Camera Usage by Other Apps
Before diving into complex troubleshooting, confirm whether another app is hogging the camera. This is often a quick fix, preventing unnecessary effort. Here’s how to check:
First, close all apps that might be using the camera, such as video calling apps (like Google Meet, Zoom, or WhatsApp), camera apps, or any app that uses the camera in the background (like some augmented reality apps). After closing these apps, try accessing the camera from the app you’re trying to use. If it works, you’ve identified the problem.
Another approach involves checking the Android system’s recent apps list. This list provides a visual overview of recently used apps. Look for any apps that might be actively using the camera. If you find one, close it, and then test the camera again in the problem app.
Finally, some Android devices have a built-in feature or indicator that shows when the camera is in use. This could be a small icon in the status bar or a notification. Consult your device’s user manual to learn how to identify this indicator.
Troubleshooting Camera Hardware Issues
Hardware failures can be more complex to address, but certain steps can help determine if the problem lies with the camera itself.
Start by visually inspecting the camera lens. Look for any obstructions, such as smudges, dirt, or cracks. Clean the lens gently with a microfiber cloth. Even a small smudge can significantly affect image quality or prevent the camera from working correctly.
Next, test the camera in multiple apps. If the camera isn’t working in any app, the problem is likely hardware-related. However, if it works in some apps but not others, the issue might be software-related (e.g., permission issues or app bugs). Try the built-in camera app; if it doesn’t work, that confirms a hardware problem.
Restart your device. Sometimes, a simple restart can resolve temporary glitches. Turn off your phone completely and then turn it back on. This can clear temporary files and refresh the system, potentially fixing minor hardware issues.
Consider a factory reset as a last resort. This will erase all data on your device, so back up your important files before proceeding. A factory reset can sometimes resolve persistent hardware or software conflicts, but it’s a drastic step and should only be taken if other troubleshooting steps have failed.
Solutions for Common Camera Access Problems
Here are some actionable solutions to tackle the camera access woes, presented in a handy blockquote.
Problem: App not granted camera permission.
Solution: Go to Settings > Apps > [App Name] > Permissions and ensure the Camera permission is enabled. If denied, enable it. If already enabled, try toggling it off and on.
Problem: Camera being used by another app.
Solution: Close all apps that might be using the camera (video call apps, camera apps, etc.). Restart the app you are trying to use.
Problem: App crashes or freezes when accessing the camera.
Solution: Clear the app’s cache and data (Settings > Apps > [App Name] > Storage > Clear Cache/Clear Data). If that doesn’t work, uninstall and reinstall the app.
Problem: Camera hardware malfunction.
Solution: Inspect the lens for damage. Restart your device. If the problem persists, try a factory reset (after backing up your data). If all else fails, seek professional repair.
Problem: Camera access restricted by parental controls or restricted profile.
Solution: Check the parental control settings or user profile settings to ensure camera access is enabled for the current profile.
Managing Camera Permissions for Specific Apps
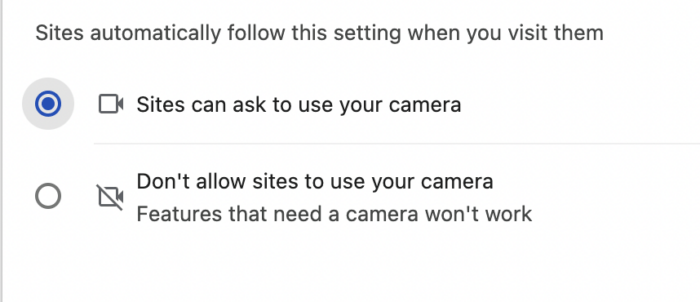
Taking control of your Android device’s camera access is like being the director of your own digital movie. You decide who gets a starring role and who remains backstage. This section delves into the nitty-gritty of managing camera permissions for individual apps, ensuring your privacy and device security remain top-notch.
Revoking Camera Permissions for an App
Sometimes, you might want to tell an app, “Lights, camera, no action!” Revoking camera permissions is your way of doing just that, preventing an app from accessing your device’s camera. This is a straightforward process, but the specific steps can vary slightly depending on your Android version.To revoke camera permissions:
- Navigate to your device’s “Settings” app. This is usually represented by a gear icon.
- Scroll down and tap on “Apps” or “Applications.” The wording might vary slightly depending on your device.
- Find the app for which you want to revoke camera access. You can either scroll through the list or use the search function.
- Tap on the app. This will open the app’s information screen.
- Tap on “Permissions.” This section displays all the permissions the app has been granted.
- Locate “Camera” and toggle the switch to the “off” position. This will revoke the app’s access to your camera. A confirmation prompt may appear.
Enabling or Disabling Camera Access for Individual Apps
Imagine you’re the gatekeeper of your camera. You have the power to decide which apps get the VIP pass and which ones are kept at bay. Enabling or disabling camera access for individual apps is the core of this control.Here’s how to enable or disable camera access for individual apps:
- Access your device’s “Settings” app, represented by the gear icon.
- Tap on “Apps” or “Applications.”
- Select the specific app for which you want to manage camera access.
- Tap on “Permissions.”
- Locate “Camera.”
- Toggle the switch next to “Camera” to enable or disable access. When the switch is on, the app has access; when it’s off, it doesn’t.
Managing Camera Permissions for System Apps
Even system apps, the essential components of your Android device, require permission management. These apps, vital for the device’s functionality, often need camera access for features like video calls or barcode scanning. Managing these permissions requires a careful balance between functionality and security.The process for managing camera permissions for system apps is nearly identical to managing permissions for third-party apps:
- Open the “Settings” app.
- Go to “Apps” or “Applications.”
- Find the system app you’re interested in. System apps may be listed separately or within a combined list. If you cannot find it, it might be hidden, and you may need to show system apps (usually from a menu in the Apps settings).
- Tap on the app to access its information screen.
- Select “Permissions.”
- Locate “Camera” and toggle the switch to grant or revoke access.
It’s important to understand the role of each system app and the potential impact of revoking camera access. For instance, revoking camera access from the phone app could prevent you from using video calling features.
Impact of Revoking Camera Access on an App’s Functionality
Revoking camera access is akin to pulling the plug on a vital piece of an app’s functionality. This action can significantly alter how an app behaves and what features it can offer. Understanding these consequences is crucial before making a decision.The impact of revoking camera access varies depending on the app:
- Apps that use the camera as a core function: For apps like Snapchat, Instagram, or any video recording application, revoking camera access will render their core features unusable. The app might display an error message, prevent the user from opening the camera interface, or simply crash.
- Apps that use the camera for secondary features: Some apps utilize the camera for features like scanning QR codes, document scanning, or profile picture uploads. Revoking access will disable these specific features, while the rest of the app’s functionality may remain intact. For example, a banking app might not allow you to scan a check if you’ve revoked camera access, but you could still manage your account otherwise.
- Apps with no camera-related features: Apps that don’t use the camera at all will be unaffected. For example, a text messaging app or a music player wouldn’t be impacted by revoked camera access.
It is essential to assess each app’s functionality before revoking camera permissions. Consider how the app uses the camera and whether you’re willing to sacrifice those features for added privacy.
Using Android’s Privacy Dashboard (If Applicable)

The Android Privacy Dashboard, if available on your device, is like having a secret agent watching over your digital life. It’s a powerful tool that offers a bird’s-eye view of how your apps are using your phone’s sensitive data, including your camera. This feature puts you firmly in control, empowering you to make informed decisions about your privacy.
Purpose of the Android Privacy Dashboard
The primary function of the Android Privacy Dashboard is to give users transparency and control over their data usage. It’s designed to show you exactly which apps are accessing your camera (and other permissions like location, microphone, etc.), and when they are doing it. This helps you identify potentially suspicious behavior or apps that are overstepping their bounds. Think of it as a personal privacy audit tool, making it easier to manage permissions and protect your personal information.
Accessing the Privacy Dashboard
Getting to the Privacy Dashboard is generally straightforward, but the exact steps can vary slightly depending on your Android version and device manufacturer. However, the general path is consistent.
- Open the Settings app: Locate the Settings app icon on your home screen or in your app drawer. It usually looks like a gear or cogwheel.
- Navigate to Privacy: Within the Settings menu, look for an option labeled “Privacy” or something similar. The wording may vary, such as “Security & Privacy” or just “Privacy.”
- Select Privacy Dashboard: Once inside the Privacy section, you should find an option called “Privacy Dashboard.” Tap on it to open the dashboard.
Once opened, the Privacy Dashboard presents a visual representation of your recent app activity, making it easy to see which apps have accessed your camera and other permissions.
Monitoring Recent Camera Access
The Privacy Dashboard displays a timeline of app activity, providing a clear overview of which apps have been using your camera. It typically presents this information in a few ways.
- Timeline View: The dashboard often shows a timeline, allowing you to see when each app accessed your camera. You can usually tap on a specific time period to see the apps that were active during that time.
- App-Centric View: You can often tap on an individual app within the dashboard to see a detailed history of its camera access. This will show you exactly when the app used the camera.
- Permission-Based View: Some dashboards allow you to view activity based on the permission itself. Selecting “Camera” will display all apps that have accessed the camera, sorted by frequency or last accessed.
This allows you to quickly spot any unexpected camera usage. For example, if you see an app accessing your camera at odd hours or without your knowledge, it might be a good idea to investigate further or review its permissions.
How the Privacy Dashboard Protects User Privacy
The Privacy Dashboard is a critical tool for safeguarding your privacy. It empowers you by providing visibility and control.
- Identifying Unwanted Access: By showing you which apps are accessing your camera, the dashboard helps you identify apps that might be using your camera without your consent or knowledge.
- Informed Decision-Making: Armed with this information, you can make informed decisions about which apps you trust and which ones you might want to limit or uninstall.
- Permission Management: The dashboard often allows you to quickly jump to the app’s permission settings, making it easy to revoke camera access for apps you no longer trust or need.
- Promoting Transparency: The very existence of the Privacy Dashboard encourages app developers to be more transparent about how they use user data, including camera access.
Essentially, the Privacy Dashboard puts you in the driver’s seat of your digital privacy, giving you the tools you need to stay safe and secure.
Camera Access and Android Versions
Navigating the world of Android camera permissions can feel like a journey through a digital time capsule. Each Android version brings its own flavor of control, privacy, and user experience, much like different models of smartphones. Understanding these shifts is crucial for anyone who uses a camera-enabled app. Let’s embark on an exploration of how Android handles camera access across different iterations, from the relatively simpler times to the increasingly sophisticated privacy measures we see today.
Comparing Methods for Managing Camera Permissions Across Different Android Versions
The methods for controlling camera access have evolved considerably across Android versions. These changes reflect a growing emphasis on user privacy and control. Initially, permissions were more broadly granted, but over time, Android has moved towards more granular control and transparency.
Differences in the User Interface for Camera Permission Settings Across Android Versions
The user interface (UI) for managing camera permissions has also seen a makeover over the years. This means the way you find and adjust these settings has changed, too. The goal is always to make it easier for users to understand and control what apps can do with their cameras.
- Android 10 (API level 29): Introduced more granular controls. Users could choose to grant permissions “While using the app,” “Only this time,” or “Deny.” This was a significant step toward enhanced user control. The settings were usually found within the app’s info page in the system settings.
- Android 11 (API level 30): Further refined the “One-time permission” feature, allowing users to grant access just once. This was a privacy-focused enhancement. The settings interface remained similar to Android 10, but the options became more prominent.
- Android 12 (API level 31): Introduced a privacy dashboard, giving users a centralized view of which apps were accessing sensitive data, including the camera and microphone. This made it easier to identify and manage potentially unwanted access. The settings could be accessed via the main Settings app under the “Privacy” section. The interface included visual indicators to show when the camera was in use.
- Android 13 (API level 33): Added a more refined permission model. Apps now needed to request permission to access media files separately. The privacy dashboard was further improved, providing more detailed information about app behavior. The settings continued to be accessible through the “Privacy” section in the main Settings app, with a cleaner and more intuitive design.
- Android 14 (API level 34): Continues to build on the privacy features introduced in previous versions. Android 14 also introduced more user control with the ability to turn on or off camera and microphone access on a system level. The interface is refined to be more user-friendly, and the privacy dashboard is enhanced to provide more granular information and controls. The settings are found in the same “Privacy” section of the main Settings app.
New Features and Improvements Related to Camera Privacy in Recent Android Updates
Recent Android updates have brought a wave of features designed to enhance camera privacy. These improvements aim to give users more control over their data and a better understanding of how apps are using their cameras.
- Privacy Dashboard: This dashboard is a central hub for viewing and managing app permissions. It displays a timeline of when apps have accessed the camera, microphone, and location data.
- Indicators for Camera Use: Visual indicators, such as a camera icon in the status bar, notify users when the camera is being accessed. This helps users quickly identify if an app is using the camera in the background.
- One-Time Permissions: This feature allows users to grant temporary access to the camera, which is particularly useful for apps that only need the camera for a single task.
- Permission Groups: Android groups permissions into logical categories, making it easier for users to understand the implications of granting access to certain features.
- Restricted Settings: Android provides options to restrict background access to the camera, limiting the ability of apps to use the camera without user interaction.
Changes in Camera Permission Management Across Android Versions
Here’s a bulleted list summarizing the evolution of camera permission management across Android versions:
- Early Android Versions: Simpler permission model with less granular control. Permissions were often granted broadly.
- Android 6.0 (Marshmallow): Introduced the runtime permissions model, allowing users to grant or deny permissions at the time of app usage.
- Android 10: Introduced “While using the app” permission, offering more control over when apps can access the camera.
- Android 11: Enhanced “One-time permission” feature for temporary access.
- Android 12: Introduced the Privacy Dashboard for centralized permission management and camera access indicators.
- Android 13: Refined permission model with separate media file access permissions.
- Android 14: Further refined privacy controls, including system-level camera and microphone access toggles. Enhanced Privacy Dashboard with more granular information and controls.
Camera Access for Specific App Types

Navigating camera permissions on Android can feel like a digital treasure hunt. The process, while generally consistent, varies slightly depending on the app type. This section breaks down how to grant camera access for social media, video conferencing, and QR code scanner apps, ensuring you’re ready to capture and connect.
Granting Camera Access to a Social Media App, How to allow access to camera on android
Social media apps, like Instagram, TikTok, and Snapchat, are built on visual communication. Therefore, camera access is crucial.
- First, locate the app icon on your device’s home screen or app drawer.
- Long-press the icon, which should reveal a context menu.
- Select “App info” or “Info”. This opens the app’s settings within your Android device’s system settings.
- Within the app info screen, find “Permissions”.
- Tap on “Permissions”. A list of the app’s requested permissions will appear.
- Locate “Camera” in the permissions list.
- Tap on “Camera”. You will likely see three options: “Allow only while using the app,” “Ask every time,” and “Don’t allow.”
- Select “Allow only while using the app” to grant camera access when the app is open and in use. This is the most common and recommended setting for social media apps.
- If you select “Ask every time,” the app will prompt you for camera permission each time you attempt to use the camera.
- Choosing “Don’t allow” will prevent the app from accessing your camera.
Consider a scenario: you want to upload a photo to Instagram. If camera permissions are not granted, the app will likely display an error message, prompting you to enable camera access in the device settings. This process described above allows you to bypass this issue.
Enabling Camera Access for a Video Conferencing App
Video conferencing apps, like Zoom, Google Meet, and Microsoft Teams, require camera access for real-time video calls.
- Initiate the same process as with social media apps: locate the app icon and long-press it.
- Select “App info” or “Info”.
- Navigate to “Permissions”.
- Tap on “Permissions” to see the app’s requested permissions.
- Find “Camera” in the permissions list.
- Tap on “Camera”. You will likely encounter the same three options: “Allow only while using the app,” “Ask every time,” and “Don’t allow.”
- Select “Allow only while using the app” to grant camera access during video calls.
- For a more secure approach, consider “Ask every time,” especially if you are concerned about potential misuse. However, this may interrupt the flow of your video conferences.
- Choosing “Don’t allow” will disable video functionality.
Real-world example: Imagine a crucial business meeting on Zoom. Without camera access, you would only be able to participate via audio, missing out on the visual cues and nonverbal communication essential for effective collaboration. Therefore, allowing camera access ensures seamless participation.
Providing a Detailed Guide for Enabling Camera Access to a QR Code Scanner App
QR code scanner apps utilize the camera to scan and decode QR codes, which contain information like website URLs, contact details, or product information.
- Locate the QR code scanner app icon and long-press it.
- Select “App info” or “Info”.
- Go to “Permissions”.
- Tap on “Permissions”.
- Locate “Camera” in the permissions list.
- Tap on “Camera”. The usual options (“Allow only while using the app,” “Ask every time,” and “Don’t allow”) will be presented.
- Choose “Allow only while using the app” to enable camera access. This is the most practical choice.
- “Ask every time” can be selected, but it may cause unnecessary interruptions when scanning codes.
- “Don’t allow” will prevent the app from scanning QR codes.
Consider this: you are at a restaurant and need to scan a QR code to view the menu. Without camera access granted to the QR code scanner app, you would be unable to access the menu, highlighting the importance of proper permissions.
